Epilepsy Surgery Cost in India
About Epilepsy Surgery
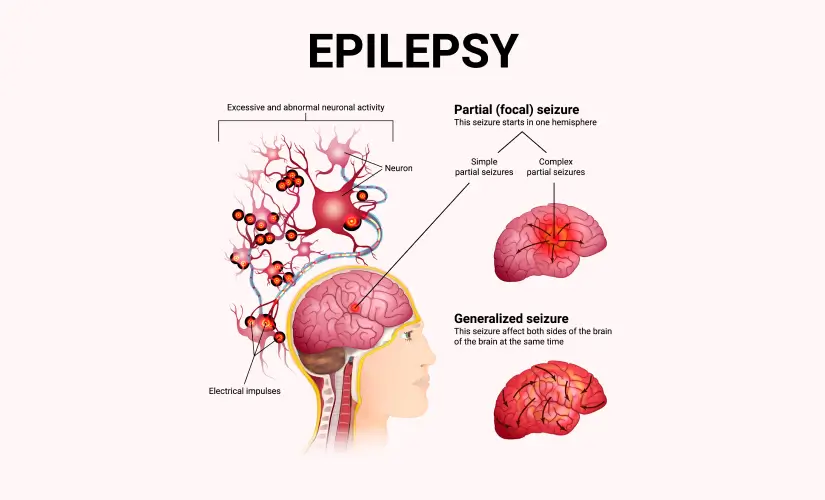
What Is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic disorder that causes a person to experience repeated, unprovoked seizures. These seizures happen due to sudden, abnormal bursts of electrical activity in the brain that interrupt normal brain function. While the exact cause isn't always known, epilepsy can result from brain injury, infections, stroke, tumors, or genetic conditions.
Seizures in epilepsy can vary widely. Some may cause a person to fall, shake uncontrollably, or lose consciousness. Others may be more subtle, such as brief moments of staring, confusion, or unusual sensations. For a diagnosis of epilepsy, a person must have had at least two unprovoked seizures that were not caused by temporary triggers like fever or low blood sugar.
Epilepsy affects people of all ages, but it often begins in childhood or later adulthood. With the right treatment protocol, most people with epilepsy can manage their condition effectively. Treatment typically starts with medications, but when drugs fail to control the seizures (especially after trying two or more types), doctors may consider surgery or device-based therapies.
Modern advances in neuroimaging and brain mapping have enabled the precise localization of seizure origins in the brain, facilitating highly targeted surgical procedures. For many patients with drug-resistant epilepsy, especially those with focal seizures, surgery offers a real chance at long-term seizure control and a better quality of life.
What Is Epilepsy Surgery?
Epilepsy surgery is a specialized medical procedure designed to help people whose seizures do not improve with medication alone. Doctors usually consider surgery when a person has drug-resistant epilepsy, meaning they've tried multiple anti-seizure medicines without success. The goal of the surgery is to either remove or disconnect the part of the brain where the seizures begin, giving the patient a better chance at leading a seizure-free life.
There are different types of epilepsy surgeries, and the choice depends on where the seizures originate and how they affect the brain. For instance, if seizures arise from a small, specific area that does not control vital functions such as speech or movement, that part may be safely removed. In other cases, doctors may perform a disconnective surgery to interrupt the abnormal signals in the brain without removing any tissue.
Unlike medications that only control seizures, surgery aims to eliminate or significantly reduce seizure activity at the source. It is not a first-line treatment, but for many patients, especially those who've suffered for years, it offers a path toward better health, independence, and overall quality of life.
What are the Different Types of Epilepsy Surgery?
Epilepsy surgery includes a range of specialized procedures designed to treat seizures. The type of surgery chosen depends on the origin of the seizures in the brain, their severity, and the patient's overall health condition. These procedures are typically performed by experienced neurosurgeons and supported by technologies such as brain imaging, intraoperative monitoring, and, in some centers, robotic assistance.
A few of the most common types of epilepsy surgeries performed worldwide are:
- Temporal Lobectomy: Temporal lobectomy is one of the most widely performed epilepsy surgeries worldwide. Surgeons remove a portion of the temporal lobe where seizures begin, usually in patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE). This type of surgery has one of the highest success rates, with up to 70–80% of patients achieving long-term seizure freedom. It is particularly effective for adults and older children who have focal seizures originating from this area.
- Lesionectomy: A lesionectomy targets a clearly identifiable lesion on brain scans, such as a tumor, cavernoma, or cortical dysplasia, that is responsible for triggering seizures. The surgeon removes only the lesion and a small margin of surrounding brain tissue. This procedure is considered highly effective when the lesion is the sole cause of seizures, and it minimizes the risk of affecting normal brain functions.
- Corpus Callosotomy: This is a disconnective surgery where the corpus callosum (a bundle of nerve fibers connecting the two halves of the brain) is partially or fully severed. It is typically performed in children with severe generalized seizures, especially drop attacks or tonic seizures that result in frequent falls and injuries. While corpus callosotomy may not completely stop seizures, it often reduces their severity and frequency, offering a safer life for the patient.
- Hemispherectomy or Hemispherotomy: Used primarily in young children with widespread seizures confined to one hemisphere of the brain, this surgery involves either removing or disconnecting one side of the brain. Conditions like Rasmussen's encephalitis or extensive cortical malformations may require this procedure. Despite its complexity, many children experience dramatic improvements in seizure control and development afterward, with the remaining hemisphere adapting over time.
- Multiple Subpial Transections (MST): When the seizure focus lies near an essential part of the brain (such as the speech or motor area) and cannot be removed, MST offers a safer option. In this technique, surgeons make tiny cuts (transections) in the brain's outer layer to disrupt seizure pathways without removing any tissue. It's less commonly used but can be effective in select cases.
- Laser Ablation Surgery (Stereotactic Laser Thermoablation): Some advanced neurology centers now offer minimally invasive laser ablation for epilepsy. The procedure involves inserting a thin laser fiber into the seizure focus and destroying the tissue using heat. The benefits include a shorter hospital stay, faster recovery, and minimal scarring. It is best suited for patients with small, well-defined seizure foci.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): Although not strictly surgical in the traditional sense, VNS involves implanting a device under the skin of the chest area that sends electrical pulses to the vagus nerve, helping reduce seizure frequency. It is often used when brain surgery is not an option.
Who Needs Epilepsy Surgery?
Not every person with epilepsy will need surgery, but for some, it becomes the best option after other treatments fail.
- Patients with Drug-Resistant Epilepsy: The primary candidates for epilepsy surgery are people who have drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE). It means they continue to experience seizures even after trying at least two appropriate anti-seizure medications at the correct doses and for a reasonable duration. Studies show that the chances of becoming seizure-free drop significantly after two failed medications, which is why surgery becomes a viable alternative at this stage.
- People with Focal Seizures: Surgery works best when seizures start from a specific area of the brain, often referred to as the seizure focus. These are known as focal or partial seizures, and they may or may not spread to other areas of the brain. If doctors can pinpoint the source of the seizure through EEG monitoring, MRI, or other imaging tests, surgery becomes a strong option.
- Patients Whose Seizures Affect Daily Life: Some individuals experience seizures that severely interfere with their daily activities, such as walking, working, attending school, or even maintaining personal safety. Frequent seizures can lead to social isolation, mental health issues, and injuries from falls or accidents. When medications do not help and quality of life suffers, doctors may recommend surgery to control the seizures and restore independence.
- Children with Developmental Risk Due to Seizures: In children, uncontrolled seizures can negatively affect brain development, learning ability, and behavior. Pediatric neurologists in India often recommend surgery early for children with severe epilepsy to protect cognitive function and promote better long-term outcomes. In such cases, early surgical intervention can lead to developmental catch-up and improved quality of life.
- Patients at Risk of SUDEP: People with frequent generalized tonic-clonic seizures may be at higher risk of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP). Reducing or eliminating seizures through surgery can significantly lower this risk. For some patients, this becomes a life-saving decision.
- Candidates Identified Through Pre-Surgical Evaluation: Before recommending surgery, hospitals in India conduct an in-depth pre-surgical evaluation, which includes continuous video EEG monitoring, MRI and PET scans, neuropsychological testing, and functional mapping (for speech, movement, and memory). Only those whose seizure origin is clearly identified and who meet safety criteria are selected for surgery.
What are the Benefits of Epilepsy Surgery?
Epilepsy surgery offers hope to individuals whose seizures remain uncontrolled despite taking multiple medications. For many of these patients, surgery can lead to life-changing improvements.
- Seizure Reduction or Elimination: The most immediate and noticeable benefit is a significant decrease in seizure frequency, and in many cases, complete seizure freedom. Depending on the type of surgery and location of the seizure focus, up to 70–80% of patients may stop having seizures altogether after surgery.
- Improved Quality of Life: When seizures become less frequent or disappear entirely, patients often find that their daily life improves dramatically. They may regain independence, return to school or work, drive again (depending on local laws), and engage more fully in social and family activities.
- Fewer or Lower Doses of Medications: Many people with epilepsy take multiple anti-seizure drugs, often leading to side effects such as fatigue, memory problems, dizziness, and mood changes. After successful surgery, some patients are able to reduce the number of medications they take or even discontinue them altogether under medical supervision.
- Cognitive and Developmental Gains in Children: Children with uncontrolled epilepsy may suffer from delayed speech, poor academic performance, and behavioral problems due to repeated seizures and medication side effects. Surgery at an appropriate age can not only reduce seizures but also improve cognitive development, learning abilities, and social interaction.
- Enhanced Emotional and Mental Health: Living with frequent seizures can cause depression, anxiety, and isolation. Many patients report feeling more optimistic and confident after surgery, especially if their seizures stop or become less frequent.
- Long-Term Stability: With appropriate post-operative care and follow-up, the results of epilepsy surgery can be long-lasting. Many patients remain seizure-free or well-controlled for years or even decades after surgery.
What are the Side Effects of Epilepsy Surgery
While epilepsy surgery offers significant benefits, like seizure reduction and improved quality of life, it is still a brain surgery, and like any surgery, it carries some risks.
- Temporary Confusion or Fatigue: After surgery, especially during the first few days, patients often experience confusion, fatigue, or drowsiness.
- Memory or Language Difficulties: Depending on the area of the brain that is affected, some individuals may experience temporary or mild issues with memory, language, or concentration.
- Weakness or Numbness: In rare cases, surgery can cause weakness, tingling, or numbness on one side of the body if motor areas of the brain are affected.
- Vision or Sensory Changes: Some patients report visual disturbances or changes in their field of vision after surgery, especially when surgery involves the occipital or temporal lobes.
- Mood and Emotional Shifts: Mood changes such as depression, anxiety, or irritability may occur temporarily after surgery. These shifts can result from changes in brain chemistry, the stress of surgery, or adjusting to a new life without seizures.
- Surgical Risks: As with any surgery, there are standard medical risks, including infection, bleeding, or reactions to anesthesia.
Recovery Timeline After Epilepsy Surgery
Recovering from epilepsy surgery is a step-by-step process that involves physical healing, mental adjustment, and ongoing medical care. While every patient's experience is slightly different, there is a general timeline most people follow. Recovery typically spans several weeks to months, depending on the type of epilepsy surgery performed and the individual's overall health.
Immediate Post-Surgery Period (0–1 Week)
After the surgery, patients usually spend a few hours in the recovery room before being transferred to a monitored hospital ward or ICU, especially if the procedure was complex. During this phase, doctors closely monitor brain function, vital signs, and the surgical site's healing progress. Mild headaches, swelling, or fatigue are common, and pain is controlled with medication.
Most epilepsy patients remain in the hospital for approximately 5 to 7 days, although more extensive procedures, such as hemispherectomy, may require a slightly more extended stay. During this time, patients begin gentle movement and are evaluated by neurologists and rehabilitation teams.
Early Recovery Phase (2–6 Weeks)
After discharge, patients continue their recovery at home or in a short-term rehabilitation center. They may still feel tired or mentally foggy, especially in the first couple of weeks. Doctors schedule follow-up visits to monitor progress, remove stitches or staples as necessary, and adjust medications as needed.
During this phase, doctors activate or fine-tune any implanted devices (like a VNS) and review seizure activity. Many patients notice a reduction in seizures soon after surgery, though full benefits may take time to appear. Light daily activities can usually resume within 2–3 weeks, but tasks requiring concentration may take longer.
Rehabilitation and Adjustment (1–3 Months)
Depending on the type of surgery, patients may require occupational therapy, physical therapy, or speech therapy. These services help improve strength, coordination, memory, and language if any deficits occurred during surgery.
Patients are also carefully monitored for emotional changes, as this is a time of mental adjustment. Some people feel a surge of confidence after gaining seizure control, while others experience anxiety about returning to everyday life.
Long-Term Recovery and Follow-Up (3 Months and Beyond)
By the three-month mark, most patients have resumed many of their everyday routines. Those who were seizure-free post-surgery often begin tapering off medications under their neurologist's guidance, though this process can take many months.
Regular follow-ups are conducted for at least one to two years to monitor brain health, medication levels, and cognitive function. In some cases, further evaluations are done if seizures persist or return.
Patients who respond well to surgery can often return to driving, working, and socializing, enjoying a better quality of life than before.
Send Query
About Epilepsy Surgery in India
What is the Cost of Epilepsy Surgery in India?
The cost of epilepsy surgery in India is more affordable compared to many Western nations, while maintaining high standards of safety and clinical outcomes. International patients often choose India for advanced neurosurgical care at a fraction of the fees charged in the US, the UK, or Europe.
The cost of epilepsy surgery in India ranges from $4,000 to $9,000, depending on several factors, including the type of surgery, hospital infrastructure, the surgeon's expertise, and the duration of the hospital stay. Here's a general breakdown by surgery type:
- The cost of a temporal lobectomy in India ranges from $5,000 to $7,000, depending on the hospital and the complexity of the surgery.
- A lesionectomy typically costs between $4,000 and $6,000, especially when the lesion is clearly defined and easily accessible.
- For patients undergoing a corpus callosotomy, the cost lies within the range of $6,000 to $8,000.
- A hemispherectomy or hemispherotomy, being a more extensive and complex surgery, is priced between $7,000 and $9,000.
- Laser ablation surgery, when available, typically costs between $6,500 and $9,000, providing a minimally invasive alternative.
- The cost of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS), including the price of the implanted device, typically ranges from $8,000 to $12,000.
These packages usually include:
- Pre-operative investigations (MRI, EEG, neuropsychological testing)
- Surgical procedure and anesthesia
- Hospital stay (typically 5–10 days)
- ICU monitoring (if required)
- Medications during admission
- Post-operative care and early follow-up
Cost Compared to Other Countries
Patients from countries like the US, Canada, the UK, and Australia often face costs ranging from $30,000 to $70,000 or more for similar procedures. It makes India an attractive option for families seeking expert care without a financial burden.
What Factors Affect the Cost of Epilepsy Surgery in India?
The overall cost of epilepsy surgery in India varies from one patient to another based on several medical and logistical factors. While the base surgical fee may be similar across hospitals, specific elements related to the patient's condition, treatment needs, and hospital preferences often influence the final cost.
- Type of Surgery Performed: The most significant cost variation comes from the kind of epilepsy surgery being performed. For example, a temporal lobectomy is usually more affordable than a hemispherectomy or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) procedure, which involves an implantable device.
- Choice of Hospital and City: Surgical expenses often differ depending on the city and hospital. Hospitals in metro cities like Mumbai or Bangalore may charge more than those in smaller towns.
- Surgeon's Experience and Team Expertise: Highly experienced neurosurgeons and comprehensive epilepsy surgery teams typically command higher fees, which can be reflected in the total treatment cost.
- Pre-Surgical Testing and Imaging: Before surgery, patients undergo a detailed evaluation that may include MRI scans, video EEG monitoring, PET or SPECT scans, and neuropsychological assessments. The number and complexity of these tests can significantly impact the total cost of treatment.
- Length of Hospital Stay and ICU Care: Some patients may require a more extended hospital stay, particularly those undergoing complex procedures or experiencing post-surgical complications.
- Type of Room and Accommodation: Private rooms, deluxe suites, and patient amenities, such as companion stay or customized meals, can also impact the total cost.
- Post-Surgical Recovery and Medications: The initial weeks after surgery may require follow-up scans, medications, and physical or cognitive rehabilitation.
Why Choose India for Epilepsy Surgery?
India is a global hub for epilepsy surgery, thanks to its unique combination of medical expertise, modern infrastructure, and affordable pricing. Patients from around the world travel to India each year seeking advanced neurological care that is both high-quality and cost-effective.
- World-Class Neurosurgeons with Global Training: India is home to a growing number of highly trained neurosurgeons who specialize in epilepsy surgery. They bring years of experience in handling complex epilepsy cases, both in adults and children, and are skilled in all relevant procedures.
- Advanced Technology and Diagnostic Tools: Leading hospitals in India are equipped with the latest technologies necessary for safe and precise epilepsy surgery. These include high-resolution MRI, video EEG monitoring, PET and SPECT scans, neuro-navigation systems, and intraoperative brain mapping.
- High Success Rates Comparable to the West: Indian hospitals consistently report seizure freedom rates of 60–80%, depending on the procedure and patient profile. In addition to reduced seizures, many patients enjoy significant improvements in mental clarity, mobility, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
- Cost-Effective Treatment Packages: One of the most compelling reasons to choose India is the dramatically lower cost of treatment. Epilepsy surgeries in India can cost 60–80% less than in Western countries, without compromising quality.
- Multilingual and Culturally Sensitive Care: Indian hospitals offer a warm and inclusive environment for international patients. Many institutions provide interpreters, multilingual staff, and culturally sensitive care, ensuring that patients and their families feel understood and respected.
- No Waiting Lists and Streamlined Process: Unlike many countries where public healthcare systems involve long wait times, epilepsy surgery in India is scheduled promptly. Once the diagnosis is confirmed and pre-surgical assessments are complete, most patients undergo surgery within a few days.
Services for International Patients
India's top hospitals and medical tourism facilitators have developed specialized services to make epilepsy surgery accessible and stress-free for patients traveling from abroad. From the moment a patient expresses interest until long after surgery, the system is designed to provide comfort, clarity, and convenience at every step.
- Medical Visa Assistance: Hospitals often issue a visa invitation letter, which helps patients secure a medical visa quickly. In many cases, visa processing is fast-tracked for those undergoing neurological treatments, especially if seizures are frequent or life-altering.
- Airport Pickup and Local Transportation: Most major hospitals offer airport pickup services to ensure patients arrive safely and comfortably. Local transportation is also arranged for follow-up visits, diagnostic tests, and discharge.
- Affordable Accommodations and Meals: Patients can choose from a range of nearby accommodations, including guesthouses and luxury hotels. Meal services are tailored to dietary needs, including vegetarian, halal, or diabetic-friendly options.
- Language Interpretation Services: Communication is crucial during treatment. That's why top hospitals provide interpreters fluent in Arabic, French, Spanish, Russian, Swahili, and more, depending on the patient's region.
- Dedicated International Patient Coordinators: Every international patient is assigned a coordinator who acts as a single point of contact throughout the medical journey. The coordinator helps with hospital admission, appointments, billing, document preparation, and discharge planning.
- Follow-Up Care: Hospitals often schedule teleconsultations after the patient returns home to check recovery progress, manage medications, and address any concerns.
- Support for Travel and Documentation: Patient coordinators help with currency exchange, insurance letters, visa extensions, and return-to-home fitness certificates.
Epilepsy Surgery Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Epilepsy Surgery costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $4,000 - $9,000 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
Leading Hospitals for Epilepsy Surgery in India

SP Medifort Hospital
SP Medifort, Thiruvananthapuram, is a JCI-accredited, 475-bed multi-super-specialty hospital spread across 500,000 sq. ft. The hospital houses 10 modu...
Accreditations


Facilities

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, is a 435-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital with 120 critical care beds. Established in 20...
Accreditations

Facilities

AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, is a 1,000-bed, JCI- and NABH-accredited super-specialty hospital spanning 1.7 million sq. ft. It is the flagshi...
Accreditations


Facilities

Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai
Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai, is a 200-bed quaternary-care hospital and part of the IHH Healthcare network, one of the world’s largest priva...
Accreditations

Facilities

MGM Healthcare, Chennai
MGM Healthcare, Chennai, is a 400-bed quaternary-care super-specialty hospital accredited by JCI, NABH, and NABL. The hospital features 100 ICU beds,...
Accreditations


Facilities

MIOT International, Chennai
MIOT International, Chennai, is a 1,000-bed NABH- and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital serving patients from more than 130 countries. Establish...
Accreditations

Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai, is the flagship hospital of the Apollo Group. Established in 1983, it has 560 beds, 46 ICUs, and 15 operating...
Accreditations



Facilities

HCG Cancer Centre, Mumbai
HCG Cancer Centre, Borivali, Mumbai, is an NABH- and AACI-accredited comprehensive cancer hospital established in 2019. The 119-bedded facility includ...
Accreditations


Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, established in 2016, is a 500-bed JCI- and NABH-accredited quaternary care hospital offering advanced treatment across...
Accreditations


Facilities

Marengo Asia Hospitals, Faridabad
Marengo Asia Hospital, formerly QRG Health City, is a 325-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital in Faridabad. It offers advanced care i...
Accreditations

Facilities
FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Related Procedures
Other procedures in this department
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
