Left Ventricular Assist Device - LVAD Cost in India
About Left Ventricular Assist Device - LVAD
What Is a Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD)?
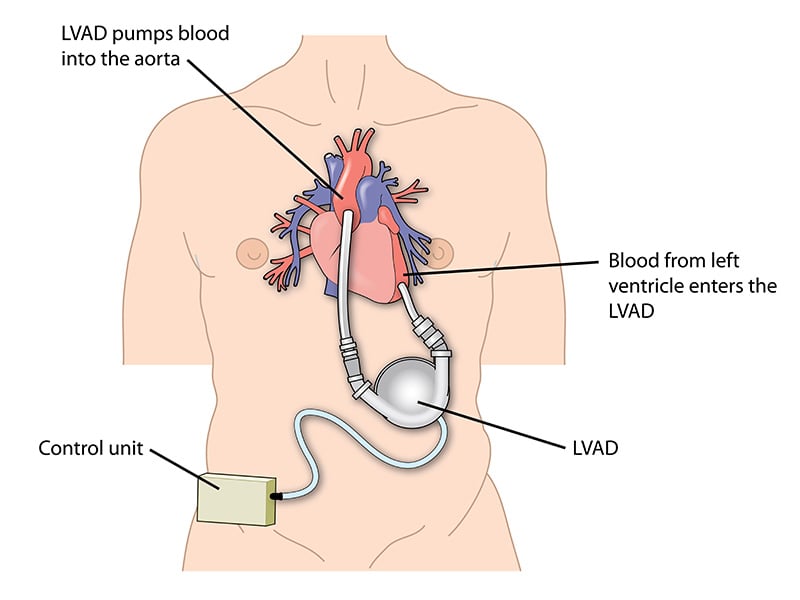
A left ventricular assist device, abbreviated as LVAD, is a mechanical pump that helps the left ventricle (the heart's main pumping chamber) circulate blood throughout the body. Doctors implant the device inside the chest during open-heart surgery. Once in place, the LVAD takes over the heart's pumping function, ensuring that oxygen-rich blood continues to flow to vital organs throughout the body.
LVADs are useful in patients with advanced heart failure, primarily when medications no longer provide relief. Unlike a total artificial heart, which replaces the entire heart, an LVAD works in conjunction with the patient's existing heart, supporting its weakened function.
The device consists of several key components:
- A pump, which is implanted inside the chest and connected to the heart.
- A driveline cable, which passes through the skin and connects the pump to the controller.
- A controller, worn outside the body, that powers and monitors the pump.
- A set of rechargeable batteries or a power unit, which keeps the system running 24/7.
LVADs have undergone significant evolution over the years. Today's models are smaller, quieter, and more efficient. Patients can live active lives with proper care, often experiencing substantial improvement in their symptoms, energy levels, and daily functioning.
Why Do Patients Need an LVAD?
Patients need a left ventricular assist device when their heart becomes too fragile to pump blood effectively on its own. This situation typically arises in end-stage heart failure, when medications and less invasive treatments no longer manage symptoms or prevent deterioration.
LVAD is not a first-line therapy. Doctors usually recommend it when a patient has tried maximum medical treatment (including ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, diuretics, and other drugs) but still struggles with fatigue, breathlessness, fluid retention, and low cardiac output. In such cases, the LVAD provides mechanical support to restore circulation and relieve the burden on the heart.
There are three main scenarios in which doctors use an LVAD:
- Bridge to Transplant: Patients who are candidates for a heart transplant but face long waiting times often receive an LVAD to stabilize their condition and keep them alive and functional until a donor's heart becomes available.
- Destination Therapy: Patients who are ineligible for a heart transplant due to age, other illnesses, or personal choice may receive an LVAD as a long-term solution. In such cases, the device acts as a permanent alternative to a transplant, often extending life by several years.
- Bridge to Recovery: In some patients, particularly those with temporary heart failure due to infections, myocarditis, or post-surgical complications, an LVAD can support the heart long enough to allow it to recover on its own. Once the heart regains its strength, doctors may remove the device.
Doctors assess each patient's medical condition, comorbidities, heart function, and overall prognosis before recommending LVAD implantation. With proper patient selection, the device can increase survival rates and improve quality of life, giving patients a second chance at life.
Who Is a Candidate for LVAD?
A patient becomes a candidate for left ventricular assist device implantation when they suffer from advanced heart failure that is no longer manageable through medications or other non-surgical treatments. Doctors consider LVAD for individuals whose heart function is severely impaired and who continue to experience debilitating symptoms despite optimized medical therapy.
Key criteria for LVAD candidacy include:
- End-Stage Heart Failure (NYHA Class III or IV): Candidates typically have New York Heart Association Class III or IV heart failure. It means they experience symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, or swelling, even at rest or with minimal physical activity.
- Reduced Ejection Fraction: Patients typically have a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of less than 25%, indicating that the heart pumps a relatively small amount of blood with each beat.
- Not Responding to Medications: Despite receiving guideline-directed heart failure medications, these patients continue to deteriorate or fail to improve.
- Eligible for Transplant (or Not): Some LVAD recipients are waiting for a heart transplant (bridge to transplant), while others are not suitable for transplantation due to age or comorbidities (destination therapy). Both groups may be eligible based on overall functional status and quality of life goals.
- No Contraindications: Patients should not have uncontrolled infections, severe kidney or liver failure, coagulation disorders, or irreversible brain damage. Those conditions could complicate surgery or impair recovery.
- Sufficient Support System: Because an LVAD requires lifelong device management, follow-ups, and attention to hygiene and power supply, the patient must have a stable home environment and caregiver support.
How Does the LVAD Implant Procedure Work?
The LVAD implant procedure is a major open-heart surgery performed under general anesthesia. It involves placing a mechanical pump inside the chest to assist the weakened left ventricle in circulating blood. The entire process typically lasts 4 to 6 hours, and the patient is closely monitored before, during, and after the operation.
Pre-Surgical Preparation
Before surgery, patients undergo a thorough evaluation that includes echocardiograms, chest X-rays, blood tests, and, in some cases, cardiac catheterization. It helps the surgical team assess heart function, lung health, and readiness for the procedure. The patient is admitted one or two days prior to surgery, and a dedicated heart failure team—including a cardiologist, cardiac surgeon, anesthetist, and device technician—creates a customized surgical plan.
Surgical Steps
- Anesthesia and Incision: The surgeon administers general anesthesia, ensuring the patient is entirely unconscious and pain-free. A midline sternotomy (an incision through the chest) is made to access the heart.
- Attachment of the LVAD Pump: The inflow cannula of the LVAD is connected to the left ventricle, and the outflow cannula is attached to the ascending aorta. This main artery distributes blood to the body. This setup allows the pump to draw blood from the failing left ventricle and deliver it directly into systemic circulation.
- Controller and Driveline Placement: A cable known as the driveline connects the internal pump to an external controller and battery pack. This cable is passed through the skin and attached to a wearable device that the patient uses daily. The controller manages pump speed and provides alerts in case of any malfunction.
- Closing the Chest: Once all connections are secure and the pump is tested for functionality, the surgical team closes the chest with sutures or surgical staples. The LVAD patient is then transferred to the cardiac intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring and care.
Postoperative Recovery
Patients remain in the cardiac ICU for 2 to 3 days and are then moved to a step-down cardiac unit. During the hospital stay, the care team monitors heart function, wound healing, infection risk, and device performance to ensure optimal patient care. Physical therapy begins early to aid in the recovery process. The total hospital stay lasts around 2 to 4 weeks, depending on the patient's condition and response to the procedure.
Doctors and nurses also provide in-depth training to patients and caregivers on how to use and maintain the LVAD, including instructions on battery changes, controller management, and emergency handling.
Send Query
About Left Ventricular Assist Device - LVAD in India
What Is the Cost of LVAD Surgery in India?
The cost of left ventricular assist device (LVAD) surgery in India typically ranges from $45,000 to $65,000 for international patients. The price is significantly lower than what the same procedure would cost in the United States or Europe, where total costs often exceed $150,000 to $200,000. Despite the lower price, patients receive high-quality care, advanced surgical techniques, and internationally approved devices.
The total price of LVAD surgery in India generally includes:
- The LVAD device (FDA- or CE-approved, such as HeartMate 3 or HeartWare HVAD)
- Surgeon's and anesthetist's fees
- Operating room charges and surgical consumables
- Cardiac ICU stay and monitoring
- Hospital stay (14 to 21 days)
- Preoperative investigations and imaging
- Postoperative care and physiotherapy
- Patient and caregiver training sessions
- Follow-up consultations during the hospital stay
Note: The price range varies depending on factors such as hospital location, surgeon's experience, duration of hospitalization, device brand, and any complications that require extended care.
LVAD Surgery Cost Breakdown in India:
Category | Estimated Cost (in USD) |
| LVAD Device (HeartMate 3 or similar) | $25,000 – $35,000 |
| Surgical Fees | $4,000 – $6,000 |
| Anesthesia & ICU Charges | $3,000 – $5,000 |
| Hospital Stay (14–21 days) | $4,000 – $6,000 |
| Preoperative Tests & Imaging | $1,500 – $2,000 |
| Surgical Consumables | $1,000 – $2,000 |
| Post-Op Medications & Therapy | $1,000 – $1,500 |
| Device Controller & Accessories | $2,500 – $3,000 |
| Patient Education & Device Training | $500 – $1,000 |
| Follow-Up During Hospital Stay | $500 – $1,000 |
Total Estimated Cost: $45,000 – $65,000
This breakdown offers a transparent view of the factors that contribute to the overall cost of LVAD surgery in India. Most hospitals provide package-based pricing, but additional charges may apply if patients require extended ICU support, have pre-existing medical conditions, or require long-term hospitalization.
International patients are advised to request all-inclusive quotes that clearly outline the currency conversion, the inclusion of companion stay, visa assistance, and post-discharge follow-up support.
What Factors Influence the Cost of LVAD in India?
Several factors influence the final price of left ventricular assist device surgery in India, despite the country already offering highly competitive prices compared to the West.
- Choice of Hospital and Location: Hospitals in metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore may charge more due to advanced infrastructure, JCI or NABH accreditations, and higher staffing costs.
- Brand and Type of LVAD Device: The cost varies depending on whether the hospital uses premium, FDA-approved devices, such as the HeartMate 3 or HeartWare HVAD. These devices are reliable and long-lasting, but they come at a higher base cost, which is reflected in the overall package.
- Experience of the Surgical Team: Highly experienced cardiac surgeons who specialize in mechanical circulatory support typically charge more. However, their involvement also increases safety, improves surgical outcomes, and reduces costs associated with complications.
- Preoperative and Postoperative Requirements: Patients with comorbidities such as diabetes, kidney disease, or lung issues may need additional diagnostic workups, ICU time, or specialist consultations, which can increase the total expense.
- Length of Hospital Stay: If complications arise or recovery is slower than expected, patients may need to stay longer in the ICU or ward, resulting in higher room, nursing, and care charges.
- Patient's Medical Condition: Patients in critical condition who require urgent surgery, multiple devices, or additional cardiac procedures, such as valve repair, may face higher overall costs due to the complexity of their condition.
Why Choose India for LVAD Implantation?
India has emerged as one of the most sought-after destinations for left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation, especially among international patients. The country combines cutting-edge medical technology, globally trained cardiac specialists, and cost-effective treatment, making it an ideal option for patients seeking advanced management of heart failure.
- World-Class Cardiac Expertise: India is home to some of the finest cardiac surgeons who specialize in mechanical circulatory support, including LVADs. Many of these experts have trained at top institutions in the US, UK, or Germany, bringing decades of experience in handling high-risk heart failure cases.
- FDA- and CE-Approved Devices: Indian hospitals utilize the latest generation of LVAD systems, including HeartMate 3 and HeartWare HVAD, which are approved by global regulatory bodies and are widely used in the West. These devices are recognized for their reliability, enhanced hemocompatibility, and reduced risk of thrombosis or stroke.
- Significant Cost Savings: LVAD surgery in India costs up to 70% less than in the United States, Canada, or Western Europe. International patients can expect complete LVAD treatment, including the device, surgery, hospital stay, ICU care, and medications, for around $45,000 to $65,000.
- Infrastructure That Matches Global Standards: Top cardiac centers in cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Bangalore offer state-of-the-art operating rooms, hybrid cath labs, and fully equipped cardiac ICUs.
- Proven Track Record with International Patients: Thousands of patients from countries such as Nigeria, Kenya, Iraq, Bangladesh, and the UAE have chosen India for LVAD surgery. High satisfaction rates, excellent outcomes, and positive word of mouth have solidified India's reputation as a global hub for heart care.
Support Services for International Patients
India offers a wide range of specialized support services to make LVAD surgery accessible, safe, and stress-free for international patients.
- Visa Assistance and Medical Invitation Letters: Most top cardiac hospitals in India offer medical visa invitation letters and assist with coordinating the necessary documentation for embassy approval.
- Airport Pickup and Local Transportation: Hospitals arrange airport pickup services in comfortable, air-conditioned vehicles. Patients and their companions are transported directly to the hospital or their accommodation without hassle.
- Language and Translation Services: India's major hospitals employ multilingual support teams and professional interpreters fluent in Arabic, French, Swahili, Russian, and other widely spoken languages.
- Affordable Accommodation Options: International desks assist with booking nearby guesthouses, serviced apartments, or hospital-based lodging that are hygienic, safe, and reasonably priced.
- Dedicated International Patient Coordinators: Every international patient is assigned a devoted case manager or patient coordinator who serves as the single point of contact. They handle scheduling, billing, pharmacy support, dietary needs, and any personal requests throughout the hospital stay.
- Post-Discharge Follow-Up and Teleconsultation: After discharge, hospitals provide regular teleconsultations to ensure the LVAD device is functioning correctly and address any concerns.
- Caregiver Training and Emergency Support: Before leaving the hospital, both patients and their caregivers undergo hands-on training in LVAD management, including changing batteries, handling alarms, and recognizing complications.
LVAD Success Rate and Life Expectancy in India
India has achieved impressive outcomes with left ventricular assist device implantation, thanks to advancements in cardiac surgery, skilled medical teams, and the availability of globally approved devices. Most leading cardiac centers in India now report success rates between 85% and 92% for LVAD procedures in carefully selected patients. These outcomes are comparable to those of top international heart institutes. Many patients who receive an LVAD as a bridge to transplant survive long enough to receive a donor's heart and experience excellent long-term outcomes. For those receiving LVAD as destination therapy, life expectancy has also increased, with studies showing survival rates of 70% at two years and 50% at five years post-implantation.
In India, the careful selection of patients, rigorous infection control measures, and continuous device monitoring have helped reduce common risks such as driveline infections or clot formation. Moreover, the use of newer-generation devices, such as the HeartMate 3, has minimized complications, including pump thrombosis and stroke.
Patients who respond well to the procedure often regain mobility, return to daily routines, and even travel, provided they manage the device correctly and adhere to medical advice. The emotional and physical burden of severe heart failure also eases significantly, allowing patients to live with greater independence and stability.
Continued improvements in device technology and postoperative care are anticipated to further enhance life expectancy and outcomes for LVAD patients in India in the years to come.
Is India a Safe Option for LVAD Surgery?
Yes, India is considered a safe and reliable destination for left ventricular assist device surgery, particularly for international patients seeking advanced cardiac care at an affordable price. The safety of LVAD implantation in India is backed by world-class infrastructure, internationally trained surgeons, and strict adherence to global healthcare standards.
Top cardiac hospitals in India follow evidence-based protocols for preoperative assessment, infection prevention, anesthesia, and post-surgical care. Many facilities are accredited by international bodies, such as the Joint Commission International (JCI) and the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals (NABH), ensuring quality assurance and patient safety at every step.
Modern hospitals in India also use advanced cardiac operating rooms, intraoperative imaging, and automated device calibration systems to reduce procedural risks. Postoperative care includes intensive monitoring in cardiac ICUs equipped with 24/7 telemetry, infection control units, and advanced life-support systems.
Infection control is a high priority, especially given the driveline involved in LVADs. Indian hospitals implement strict wound care protocols and educate patients on proper home hygiene and device maintenance to prevent complications.
International patients receive additional safety support through dedicated case managers, interpreters, and round-the-clock access to their medical teams. These services ensure that patients feel safe, informed, and cared for throughout their entire experience, from arrival to discharge and beyond.
Recovery Process and Timeline After LVAD Surgery
Recovery after left ventricular assist device surgery is gradual, but with proper care, patients can regain independence and resume many everyday activities.
Immediate Post-Surgery Phase (Week 1–2)
After surgery, the patient is transferred to the cardiac intensive care unit (ICU), where doctors closely monitor vital signs, device function, and heart performance. The ICU stay typically lasts 2 to 4 days, depending on the patient's response and condition.
Once stable, the patient is shifted to a step-down cardiac care unit for continued monitoring and early mobilization. Nurses help patients start with light physical activity and respiratory therapy to prevent complications such as pneumonia or blood clots.
Doctors begin training the patient and caregiver on how to manage the LVAD device, including how to respond to alarms, replace batteries, and care for the driveline exit site to prevent infection.
Hospital Stay and Discharge (Week 2–3)
Most patients stay in the hospital for around 14 to 21 days. Before discharge, they must demonstrate a good understanding of LVAD care. The hospital team also evaluates wound healing, organ function, and psychological readiness. A detailed care plan is provided, including medication schedules, dressing instructions, and emergency protocols.
By the time of discharge, most patients can walk short distances, climb a few stairs, and perform basic self-care tasks. The device settings are optimized, and telemonitoring is often arranged for follow-up from the patient's home country.
Recovery at Home (Month 1–3)
Once home, the patient needs a quiet, clean environment and assistance from a trained caregiver. Regular dressing changes, adherence to medication, and avoiding heavy lifting are essential. Most patients regain strength gradually and can resume light household activities within a few weeks.
Mid- to Long-Term Recovery (After 3 Months)
By three months, most patients see significant improvements in breathing, energy levels, and overall mobility. Many work-from-home tasks can be performed remotely, including attending social events and even traveling, provided they carry backup equipment and maintain strict device hygiene practices.
After six months, many LVAD patients reach a stable recovery stage. If the LVAD was implanted as a bridge to transplant, the transplant listing process may begin. If it was intended as destination therapy, patients continue with long-term monitoring and support.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Ongoing Care
While LVADs restore circulation and extend life, patients must adapt to a new lifestyle. They need to avoid swimming, extreme sports, and exposure to magnetic fields. They also require lifelong anticoagulation (blood thinning) and regular blood tests.
With good care, most LVAD patients in India live for 5 to 10 years or longer, depending on their underlying condition and how well they follow medical advice.
Left Ventricular Assist Device - LVAD Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Left Ventricular Assist Device - LVAD costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $45,000 - $65,000 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
Leading Hospitals for Left Ventricular Assist Device - LVAD in India

SP Medifort Hospital
SP Medifort, Thiruvananthapuram, is a JCI-accredited, 475-bed multi-super-specialty hospital spread across 500,000 sq. ft. The hospital houses 10 modu...
Accreditations


Facilities

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, is a 435-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital with 120 critical care beds. Established in 20...
Accreditations

Facilities

AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, is a 1,000-bed, JCI- and NABH-accredited super-specialty hospital spanning 1.7 million sq. ft. It is the flagshi...
Accreditations


Facilities

Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai
Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai, is a 200-bed quaternary-care hospital and part of the IHH Healthcare network, one of the world’s largest priva...
Accreditations

Facilities

MGM Healthcare, Chennai
MGM Healthcare, Chennai, is a 400-bed quaternary-care super-specialty hospital accredited by JCI, NABH, and NABL. The hospital features 100 ICU beds,...
Accreditations


Facilities

MIOT International, Chennai
MIOT International, Chennai, is a 1,000-bed NABH- and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital serving patients from more than 130 countries. Establish...
Accreditations

Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai, is the flagship hospital of the Apollo Group. Established in 1983, it has 560 beds, 46 ICUs, and 15 operating...
Accreditations



Facilities

HCG Cancer Centre, Mumbai
HCG Cancer Centre, Borivali, Mumbai, is an NABH- and AACI-accredited comprehensive cancer hospital established in 2019. The 119-bedded facility includ...
Accreditations


Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, established in 2016, is a 500-bed JCI- and NABH-accredited quaternary care hospital offering advanced treatment across...
Accreditations


Facilities

Marengo Asia Hospitals, Faridabad
Marengo Asia Hospital, formerly QRG Health City, is a 325-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital in Faridabad. It offers advanced care i...
Accreditations

Facilities
FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Related Procedures
Other procedures in this department
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
