Prostate Cancer Treatment Cost in India
About Prostate Cancer Treatment
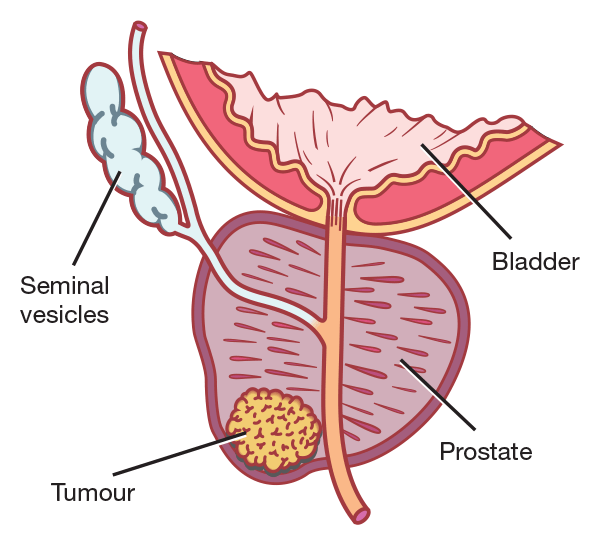
What Is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is a common type of men's only cancer that develops in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped organ that sits just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. This gland plays a vital role in producing seminal fluid. This fluid is responsible for nourishing and transporting sperm during ejaculation. Prostate cancer develops when abnormal cells in the prostate begin to grow uncontrollably, often forming a tumor. While many cases develop slowly and may not pose an immediate threat, some can be aggressive and move quickly to other body parts, such as the bones, lymph nodes, or liver.
This disease primarily affects older men, typically those above 50, but it can also appear earlier in men with a family history or specific genetic mutations. Due to its generally slow progression in the early stages, prostate cancer might go unnoticed for years without causing symptoms, making regular screening essential, especially for high-risk individuals.
Types of Prostate Cancer
Not all prostate cancers are the same. The type of cancer depends on which prostate cells are affected.
- Adenocarcinoma: This is by far the most common form of prostate cancer, accounting for nearly 95% of all cases. It begins in the glandular cells that produce prostate fluid. It can be further classified into acinar and ductal adenocarcinomas.
- Small Cell Carcinoma: A rare but aggressive type of prostate cancer that grows rapidly and often spreads beyond the prostate by the time it's diagnosed. It doesn't typically raise PSA levels, which can delay detection.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Another uncommon form that originates in the flat cells of the prostate. It tends to be more aggressive than adenocarcinoma and may not respond well to hormone therapy.
- Transitional Cell Carcinoma: This rare cancer starts in the urethra and may extend into the prostate. It is usually treated differently from traditional prostate adenocarcinoma.
- Sarcomas and Other Rare Tumors: These arise from the connective tissues or muscle cells within the prostate and are extremely rare.
What are the Common Signs and Symptoms of Prostate Cancer?
In the early stages, prostate cancer causes no noticeable symptoms. As the tumor grows or spreads, men may begin to experience the following:
- Urinary Problems: These include difficulty starting or stopping urination, a weak urine stream, frequent urination (especially at night), or a feeling that the bladder isn't entirely empty.
- Pain or Burning Sensation: Discomfort during urination or ejaculation may occur in some cases.
- Blood in Urine or Semen: While not always present, this symptom should never be ignored.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Difficulty having or maintaining an erection can sometimes be linked to prostate cancer, although many other factors may contribute to this issue.
- Pelvic or Lower Back Pain: If the cancer has spread to nearby tissues or bones, it may cause persistent pain in the hips, thighs, or spine.
Because many of these symptoms can also be caused by non-cancerous prostate issues like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis, proper medical evaluation is essential to determine the actual cause.
How Is Prostate Cancer Diagnosed?
Diagnosing prostate cancer involves several steps that help doctors confirm the presence of cancer, understand its stage, and determine the most suitable treatment approach. Since early-stage prostate cancer rarely shows symptoms, routine screening plays a key role in detection, especially for men over 50 or those with a family history.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): The first step is often a digital rectal exam, where a doctor gently inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate gland. This quick procedure helps identify any irregularities like hard spots, lumps, or asymmetry that may indicate cancer. While not definitive, any abnormal findings usually lead to further testing.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Blood Test: A PSA test measures the amount of prostate-specific antigen (a protein made by prostate cells) in the blood. High PSA levels can be a mark of prostate cancer, though they may also result from non-cancerous conditions like prostatitis or BPH. Doctors consider PSA trends, age, and prostate size before recommending more invasive procedures.
- MRI or Transrectal Ultrasound (TRUS): If PSA levels are high or the DRE is abnormal, imaging tests like multiparametric MRI or transrectal ultrasound may be done to get detailed pictures of the prostate. These scans help pinpoint suspicious areas and guide the next step—biopsy.
- Prostate Biopsy: A biopsy is the most accurate way to confirm prostate cancer. It involves taking small tissue samples from the prostate using a needle, typically guided by ultrasound or MRI. These samples are sent to a lab, where a pathologist looks for cancer cells and assigns a Gleason score. This score tells how aggressive the prostate cancer appears under a microscope.
What Are the Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer?
Cancer treatment depends on the stage and grade of the disease, the patient's age, overall health, and how aggressively the cancer is likely to grow. Some cases require immediate, aggressive therapy, while others can be safely monitored. Here's a detailed look at the available treatment approaches:
Active Surveillance and Watchful Waiting
For slow-growing or early-stage prostate cancers, doctors may recommend active surveillance. It means closely monitoring the cancer with regular PSA tests, digital rectal exams, and occasional biopsies, without starting treatment unless the tumor shows signs of progressing. Watchful waiting is a more passive approach typically used when the patient is unlikely to benefit from curative treatment due to age or frailty.
Surgery (Radical Prostatectomy)
In radical prostatectomy, the surgeon completely removes the prostate gland and sometimes nearby lymph nodes. It is most often recommended for localized cancer in healthy patients. It can be performed using:
- Open surgery involves a larger incision in the lower abdomen.
- Laparoscopic surgery uses minor cuts and a camera.
- Robotic-assisted surgery, such as Da Vinci surgery, allows high precision and faster recovery.
Surgery is effective but can have side effects like urinary incontinence or erectile dysfunction, depending on the technique and nerves involved.
Radiation Therapy
This treatment uses high-energy rays or beams to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. It can be used alone or after surgery if there's a risk the cancer has returned or spread. The two main types are:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) – Directed at the prostate from outside the body.
- Brachytherapy (Internal Radiation) – Involves placing radioactive seeds directly into the prostate.
Modern radiation techniques like IMRT (intensity-modulated) or proton therapy can reduce damage to surrounding tissues.
Hormone Therapy (Androgen Deprivation Therapy)
Prostate cancer cells rely on male hormones (testosterone) to grow. Hormone therapy either reduces hormone levels or blocks their effect. It's commonly used in advanced or metastatic prostate cancer. Methods include:
- Medications to block hormone production (e.g., LHRH agonists).
- Anti-androgens prevent testosterone from binding to cancer cells.
- Surgical removal of the testicles (orchiectomy) in some cases.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is typically used for advanced-stage or castration-resistant prostate cancer not responding to hormone therapy. Drugs like docetaxel or cabazitaxel are administered via IV to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. Side effects vary but often include fatigue, nausea, and low blood counts.
Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Sipuleucel-T is a type of immunotherapy designed explicitly for prostate cancer, used in selected advanced cases. PARP inhibitors and other targeted agents may be effective for cancers with specific genetic mutations.
Focal Therapy
Emerging treatments like HIFU (High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound) or cryoablation aim to treat only the cancerous part of the prostate, minimizing side effects. These are mostly experimental or suitable for early-stage cases.
Send Query
About Prostate Cancer Treatment in India
What Is the Cost of Prostate Cancer Treatment in India?
The cost of prostate cancer treatment in India is significantly lower than in many developed countries, making it a preferred destination for international patients seeking high-quality yet affordable care. On average, prostate cancer treatment in India ranges from $3,000 to $10,000, depending on the treatment type, hospital, and city.
Here's a cost breakdown by treatment type:
- Active Surveillance: The cost of active surveillance and diagnostic monitoring for prostate cancer in India ranges from $500 to $1,000, which typically includes PSA blood tests, prostate MRI scans, and periodic biopsies to track cancer progression.
- Radical Prostatectomy: A radical prostatectomy, whether performed as an open, laparoscopic, or robotic-assisted surgery, generally costs between $4,000 and $7,500, depending on the hospital, technology used, and the surgeon's expertise.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: For those opting for external beam radiation therapy (including advanced techniques like IMRT or IGRT), the cost for a complete treatment cycle typically falls between $3,500 and $6,000.
- Brachytherapy: Brachytherapy, which involves placing radioactive seeds directly into the prostate, is priced around $5,000 to $7,000, offering a highly targeted approach with fewer sessions.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy, also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), usually involves medications taken over six months and can cost between $1,200 and $2,000.
- Chemotherapy: If chemotherapy is required, the price for six cycles of standard drugs generally ranges from $3,000 to $5,000. It can vary based on drug type and patient response.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy, such as Sipuleucel-T (if available), is among the costlier options, with treatment pricing between $10,000 and $14,000 due to the specialized nature of the therapy.
- HIFU or Cryotherapy: For minimally invasive options like High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) or cryotherapy, commonly categorized under focal therapies, the cost ranges from $4,000 to $6,500, depending on the case complexity and technology used.
What's included in the treatment package?
Most hospitals offer all-inclusive treatment packages that may cover:
- Doctor consultations and surgical fees
- Pre-operative tests and scans
- Hospital stay (typically 3–7 days)
- Operation theatre charges and ICU care
- Post-operative medications and nursing
- Follow-up visits and pathology reports
Note: Prices listed above are in USD. Indian hospitals typically bill in INR, and currency fluctuations may slightly affect the final amount at the time of payment.
Cost Comparison: India vs. Other Countries
India is one of the most cost-effective options for prostate cancer treatment globally. Patients from the US, UK, Canada, Australia, and the Middle East often choose India for its blend of affordability, cutting-edge technology, and experienced oncology teams.
Treatment Type | India | USA | UK | UAE | Thailand |
| Radical Prostatectomy | $4,000 – $7,500 | $35,000 – $45,000 | $20,000 – $28,000 | $18,000 – $24,000 | $8,000 – $11,000 |
| Radiation Therapy (IMRT/IGRT) | $3,500 – $6,000 | $30,000 – $40,000 | $22,000 – $30,000 | $14,000 – $20,000 | $7,000 – $9,000 |
| Brachytherapy | $5,000 – $7,000 | $35,000 – $50,000 | $25,000 – $33,000 | $16,000 – $21,000 | $9,000 – $12,000 |
| Hormone Therapy (6-month cycle) | $1,200 – $2,000 | $8,000 – $12,000 | $6,000 – $9,000 | $5,000 – $7,000 | $3,500 – $4,500 |
| Chemotherapy (6 cycles) | $3,000 – $5,000 | $20,000 – $30,000 | $15,000 – $22,000 | $10,000 – $15,000 | $6,000 – $8,000 |
| Immunotherapy (Sipuleucel-T) | $10,000 – $14,000 | $90,000 – $120,000 | $70,000 – $100,000 | $50,000 – $80,000 | $15,000 – $25,000 |
As the table shows, treatment in India often costs 70–80% less than in the United States or the UK, without compromising on the standard of care. This cost difference becomes even more substantial when considering longer-term treatments like hormone therapy or chemotherapy.
What are the Factors Affecting Prostate Cancer Treatment Cost in India?
The overall cost of prostate cancer treatment in India varies widely depending on several critical factors. Understanding these variables can help international patients make informed decisions and plan their medical travel more efficiently.
- Type and Stage of Prostate Cancer: Localized prostate cancer may only require surgery or radiation, while advanced cases might need multimodal treatment (e.g., hormone therapy plus chemotherapy), increasing the overall expense.
- Type of Treatment Chosen: Surgical procedures, such as radical prostatectomy, are generally less expensive than advanced therapies like proton beam radiation or immunotherapy.
- Hospital and City: Top-tier multispecialty hospitals in metro cities like Mumbai, Bangalore, and Chennai may charge more due to their high-end infrastructure, international accreditations, and technology.
- Experience of the Oncologist and Surgeon: Highly experienced cancer specialists and urologic surgeons often charge higher consultation and procedure fees. However, their expertise can significantly improve clinical outcomes, making it a worthwhile investment.
- Technology and Equipment Used: The Use of advanced robotic systems, image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT), or high-precision diagnostic tools can increase the cost slightly.
- Duration of Hospital Stay and Recovery Needs: A more extended hospital stay adds to the total bill. The need for post-operative intensive care, physiotherapy, or rehabilitation can also impact the cost.
- Type of Room and Services Opted: Choosing a deluxe or private room, using concierge services, and availing premium food or accommodation options can all add to the final hospital charges.
Why Choose India for Prostate Cancer Treatment?
India is a global hub for prostate cancer treatment, offering patients high-quality medical care at a fraction of the cost they might pay in countries like the USA, UK, or Australia. Patients from across the globe are increasingly choosing India for their cancer treatment, not only due to affordability, but also for the country's clinical excellence and advanced infrastructure.
- One of the major benefits is the availability of experienced oncologists and urologists who specialize in prostate cancer and are trained in both traditional and cutting-edge techniques such as robotic-assisted surgeries, IMRT, and HIFU.
- Indian hospitals are equipped with state-of-the-art technology, including Da Vinci robotic surgical systems, PET-CT scanners, and advanced radiation machines. These tools allow for precise diagnostics and minimally invasive procedures.
- Another significant advantage is personalized care plans. Whether a patient needs surgery, radiation, hormonal therapy, or a combination of treatments, Indian cancer centers are adept at customizing treatment protocols based on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer.
- Shorter waiting periods are also a compelling benefit. Unlike many Western countries where patients may wait weeks or even months for surgery or radiation, Indian hospitals typically offer immediate scheduling, ensuring that treatment begins promptly.
- Moreover, cost-effectiveness does not compromise quality. The affordability of treatment in India is due to lower administrative costs, lower cost of living, and government support for the healthcare sector, not a reflection of substandard care.
What Services Are Available For International Patients Seeking Prostate Cancer Treatment in India?
Hospitals in India are well-prepared to serve international patients seeking prostate cancer treatment. Dedicated international desks are available in most top hospitals, providing:
- Medical Visa Assistance: Indian hospitals provide official invitation letters and guidance to help patients and their companions obtain a medical visa quickly and smoothly.
- Airport Pickup and Drop: Hospitals arrange safe, reliable airport transfers to and from the medical facility, ensuring a stress-free arrival and departure for overseas patients.
- Accommodation Support: Patients can access assistance in booking nearby hotels, guesthouses, or serviced apartments that suit their budget and preferences during treatment.
- Language Interpretation Services: Multilingual interpreters are available to help patients and families communicate clearly with doctors, nurses, and hospital staff throughout their stay.
- Dedicated Care Coordinators: Each international patient is assigned a personal coordinator to assist with medical appointments, paperwork, billing, and daily logistics.
- Teleconsultation and Second Opinions: Before traveling, patients can schedule virtual consultations or request second opinions from top specialists to plan their treatment confidently.
- Post-Treatment Follow-Up Support: Hospitals offer ongoing care after discharge through telemedicine, report sharing, and remote guidance to ensure a smooth recovery at home.
Prognosis and Survival Rates for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer generally has a favorable prognosis, especially when diagnosed early. For localized and regional stages, the five-year survival rate is close to 100%. Even for advanced or metastatic cases, modern treatments have helped extend life expectancy and improve daily functioning.
Low-risk cases managed through active surveillance often show slow progression and minimal impact on lifespan. More aggressive forms can still be treated effectively with surgery, radiation, hormone therapy, or a combination of approaches. India's experienced cancer specialists and access to advanced technologies contribute to high treatment success rates, even in complex cases.
Recovery Timeline After Prostate Cancer Treatment
The recovery timeline after prostate cancer treatment largely depends on the type of therapy received and the patient's overall health. Each treatment approach has a unique post-treatment healing phase, and patients are closely monitored to ensure optimal outcomes.
Surgery (Open, Laparoscopic, or Robotic Prostatectomy): After surgery, most prostate cancer patients remain in the hospital for 3 to 5 days. Catheter use is common for about a week. Light activities can generally be resumed within 2 weeks, while full recovery (including return to work and exercise) typically takes 4 to 6 weeks. Patients may also experience temporary urinary or sexual side effects that gradually improve with time.
Radiation Therapy (IMRT, IGRT, or Brachytherapy): Radiation treatments are usually outpatient procedures, with each session lasting just a few minutes. While there is no significant downtime, patients may experience fatigue over several weeks. Side effects like urinary urgency or bowel changes may occur, but often resolve post-treatment.
Hormone Therapy or Chemotherapy: These treatments may not require hospitalization, but can lead to systemic side effects such as fatigue, hot flashes, or weakened immunity. Recovery is often gradual and occurs alongside treatment. Most patients continue their daily routines with some modifications during the course.
Minimally Invasive Procedures (HIFU, Cryotherapy): These focal therapies offer much quicker recovery. Patients can return to light activities within a few days and resume everyday routines in about 1 to 2 weeks. Minimal discomfort and fewer complications make these suitable for early-stage or localized cases.
Long-Term Follow-Up: Regardless of the treatment, patients will require regular follow-ups that include PSA blood tests, imaging, and consultations. This ongoing monitoring is essential to track remission, detect recurrence early, and manage any delayed side effects.
Prostate Cancer Treatment Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Prostate Cancer Treatment costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $3,000 - $10,000 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
Leading Hospitals for Prostate Cancer Treatment in India

SP Medifort Hospital
SP Medifort, Thiruvananthapuram, is a JCI-accredited, 475-bed multi-super-specialty hospital spread across 500,000 sq. ft. The hospital houses 10 modu...
Accreditations


Facilities

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, is a 435-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital with 120 critical care beds. Established in 20...
Accreditations

Facilities

AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, is a 1,000-bed, JCI- and NABH-accredited super-specialty hospital spanning 1.7 million sq. ft. It is the flagshi...
Accreditations


Facilities

Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai
Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai, is a 200-bed quaternary-care hospital and part of the IHH Healthcare network, one of the world’s largest priva...
Accreditations

Facilities

MGM Healthcare, Chennai
MGM Healthcare, Chennai, is a 400-bed quaternary-care super-specialty hospital accredited by JCI, NABH, and NABL. The hospital features 100 ICU beds,...
Accreditations


Facilities

MIOT International, Chennai
MIOT International, Chennai, is a 1,000-bed NABH- and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital serving patients from more than 130 countries. Establish...
Accreditations

Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai, is the flagship hospital of the Apollo Group. Established in 1983, it has 560 beds, 46 ICUs, and 15 operating...
Accreditations



Facilities

HCG Cancer Centre, Mumbai
HCG Cancer Centre, Borivali, Mumbai, is an NABH- and AACI-accredited comprehensive cancer hospital established in 2019. The 119-bedded facility includ...
Accreditations


Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, established in 2016, is a 500-bed JCI- and NABH-accredited quaternary care hospital offering advanced treatment across...
Accreditations


Facilities

Marengo Asia Hospitals, Faridabad
Marengo Asia Hospital, formerly QRG Health City, is a 325-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital in Faridabad. It offers advanced care i...
Accreditations

Facilities
FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Related Procedures
Other procedures in this department
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
