Total Hip Replacement - THR Cost in India
About Total Hip Replacement - THR
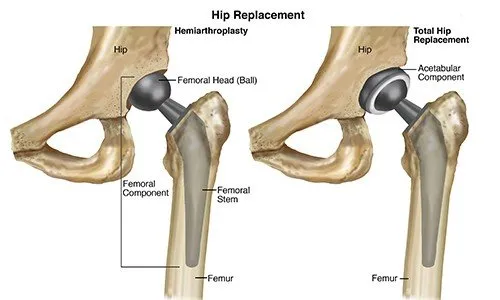
What Is a Total Hip Replacement and Why Is It Done?
Total hip replacement (THR), also known as total hip arthroplasty, is a complex surgical procedure in which a damaged hip joint is replaced with man-made components. It is performed to relieve persistent hip pain and stiffness that no longer responds to medication or physical therapy.
The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint. The ball, which is the femoral head, fits into the socket (acetabulum) of the pelvis. In conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, or hip fractures, this joint can wear out or become damaged. As a result, patients may experience intense pain, swelling, restricted movement, and difficulty walking or sitting for long durations.
During THR, the orthopedic surgeon removes the damaged parts of the hip joint and replaces them with a combination of metal, ceramic, or high-grade plastic implants. The artificial hip joint is designed to replicate the natural function of the hip, enhancing mobility and improving quality of life.
Most patients who undergo total hip replacement regain their ability to walk pain-free and return to normal activities within a few months. It is especially recommended when pain disrupts sleep, limits independence, or affects daily living despite conservative treatment.
What Are the Different Types of Hip Replacements?
Total hip replacement surgery is not a one-size-fits-all procedure. Depending on the patient's condition, age, lifestyle, and bone structure, orthopedic surgeons recommend different types of hip replacement techniques. Each type involves replacing the hip joint, but the surgical approach, implant material, and fixation method can vary.
Total Hip Replacement (Conventional THR)
It is the most commonly performed type. THR involves replacing both the femoral head (the ball) and the acetabulum (the socket) with artificial components. THR is ideal for patients with severe arthritis, joint degeneration, or multiple fractures. Recovery is reliable, and long-term outcomes are excellent when performed with modern implants.
Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty)
In this version, only the femoral head (ball) is replaced, while the socket remains intact. Partial hip replacement is typically performed in elderly patients with a fractured hip but healthy socket cartilage. It involves a shorter surgery and quicker recovery, but may not be suitable for arthritis-related damage.
Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement
This surgical technique uses a smaller incision (~2 inches) compared to traditional surgery, resulting in less tissue damage, reduced pain, and faster healing. Minimally invasive approaches are used in both total and partial replacements, but they require highly skilled surgeons and proper patient selection.
Bilateral Hip Replacement
Also known as a double hip replacement, this procedure is performed when both hips are severely affected and require surgery. It can be done in a single stage or in two stages spaced a few weeks apart. While it involves a longer recovery, it improves hip joint mobility and quality of life for patients with advanced bilateral hip disease.
Revision Hip Replacement
It is a more complex surgery done when a previous hip implant fails due to wear, infection, or loosening. The surgery involves removing the old prosthesis and replacing it with a new one. The procedure is technically demanding and typically costlier than a primary hip replacement.
Cemented vs. Uncemented Fixation
In cemented hip replacement, bone cement is used to anchor the prosthetic parts to the bone. In uncemented implants, the components are press-fit into the bone, allowing natural bone growth to secure them over time. Younger patients often receive uncemented implants, while older adults may benefit from cemented ones for quicker fixation and stability.
How Is Total Hip Replacement Surgery Performed?
Total hip replacement surgery is a well-planned and carefully executed procedure that replaces the damaged hip joint with a new artificial one. The goal is to restore joint function, relieve pain, and allow the THR patients to return to a more active, pain-free life.
- Preoperative Preparation: Before surgery, the patient undergoes a comprehensive medical evaluation, which includes blood tests, an ECG, a chest X-ray, and imaging scans such as an X-ray or MRI of the hip. The orthopedic team explains the procedure, answers questions, and obtains informed consent. On the day of surgery, the patient is admitted, and the surgical site is cleaned and marked.
- Anesthesia Administration: The anesthesiologist administers either spinal anesthesia (numbing the lower half of the body) or general anesthesia (putting the patient to sleep).
- Surgical Incision and Access: Once anesthesia takes effect, the surgeon makes a precise incision near the side or back of the hip. The location and size of the incision depend on whether a traditional or minimally invasive technique is being used. The surgeon gently separates the muscles and tissues to expose the hip joint.
- Removal of the Damaged Bone: Next, the surgeon dislocates the hip joint to remove the damaged femoral head (ball of the thigh bone) and prepares the acetabulum (hip socket). The worn-out cartilage and bone are cleaned thoroughly, creating space for the new artificial socket.
- Insertion of Artificial Components: The surgeon inserts a metal cup (socket component) into the acetabulum, often with a plastic or ceramic liner inside. Then, the femoral stem is placed into the hollow center of the thigh bone. A metal or ceramic ball is fixed on top of this stem, forming the new joint.
- Joint Realignment and Closure: After placing all components, the surgeon carefully repositions the new ball into the socket, creating a stable artificial hip joint. The movement and alignment are tested to ensure a smooth range of motion. Once confirmed, the surgeon closes the incision in layers using absorbable stitches or staples and covers it with a sterile dressing.
- Postoperative Care: The patient is taken to the recovery room, where nurses and doctors monitor vital signs and ensure the anesthesia wears off safely. Pain management begins immediately, and physical therapy is started within 24 hours to prevent stiffness and promote mobility.
The entire procedure usually takes 1.5 to 2.5 hours. Thanks to advances in surgical techniques, blood loss is reduced, and the risk of infection is minimized when procedures are performed in specialized orthopedic centers.
What Are the Different Types of Implants Used in Total Hip Replacement?
Choosing the right implant is one of the most critical decisions in total hip replacement surgery. Implants are designed to mimic the natural ball-and-socket movement of the hip joint and are made from strong, durable materials that can withstand years of use. The selection depends on factors like the patient's age, activity level, bone strength, and budget.
Metal-on-Polyethylene (MoP)
It is the most widely used and cost-effective option. The femoral head (ball) is made of metal, and the socket liner is made from a durable plastic called polyethylene.
- Best for: Older patients and those with moderate activity levels
- Advantages: Affordable, reliable, long track record of success
- Limitations: May wear down faster in very active patients
Ceramic-on-Polyethylene
In this type, the ball is made of ceramic material while the socket is lined with polyethylene. It offers better wear resistance than metal-on-polyethylene implants.
- Best for: Middle-aged patients who want a balance of durability and affordability
- Advantages: Lower wear rate, reduced risk of inflammation
- Limitations: Slightly costlier than metal-based implants
Ceramic-on-Ceramic (CoC)
Both the ball and socket components are made of ceramic. This combination is highly durable and ideal for younger, more active individuals.
- Best for: Younger patients with high activity demands
- Advantages: Very low wear rate, excellent biocompatibility
- Limitations: Higher cost; risk of implant squeaking in rare cases
Metal-on-Metal (MoM)
This design features components made from both metal and other materials. It was once popular for younger patients but is now rarely used due to safety concerns.
- Best for: Previously considered for active adults
- Advantages: Less wear; no plastic particles
- Limitations: Can release metal ions into the bloodstream; not widely recommended today
Hybrid Implants
Hybrid implants utilize a combination of fixation methods, such as a cemented socket with an uncemented femoral stem. They are customized based on the patient's bone quality and surgeon preference.
- Best for: Patients with uneven bone density or specific anatomical needs
- Advantages: Offers surgical flexibility
- Limitations: Selection depends heavily on individual case evaluation
Your orthopedic surgeon will choose the best implant type after evaluating your joint condition, age, and expected activity level. All major Indian hospitals offer a wide range of implant brands, including Zimmer Biomet, Stryker, Depuy Synthes, Smith & Nephew, and Meril.
Send Query
About Total Hip Replacement - THR in India
What is the Cost of a Total Hip Replacement in India?
The cost of total hip replacement surgery in India ranges from ₹3,00,000 to ₹5,00,000 (approximately $3,600 to $6,000). The price depends on several factors, including the type of implant used, the hospital's reputation, the surgeon's expertise, and whether the surgery is unilateral (one hip) or bilateral (both hips).
Most hospitals in India offer all-inclusive packages for international patients, which cover the complete surgical process and immediate postoperative care. These packages are designed to ensure transparency and convenience.
The typical cost includes:
- Preoperative investigations like X-rays, blood tests, ECG, and anesthesia evaluation.
- Surgeon and anesthetist fees, covering consultation, procedure, and post-op visits.
- Operation theatre charges and surgical consumables required during the procedure.
- The cost of the implant, which may be metallic, ceramic, or a hybrid material.
- Hospital stay of 5 to 7 days in a private room, including nursing care, meals, and monitoring.
- Medications and pain management during admission.
- Physiotherapy sessions during the hospital stay to start early mobilization.
- Initial post-discharge consultations are typically scheduled within 10 to 15 days of surgery.
The above-mentioned cost range applies to standard, complication-free procedures. Additional charges may apply if the patient requires ICU care, longer hospitalization, or treatment for pre-existing conditions such as diabetes or heart disease.
Breakdown of Total Hip Replacement Cost in India
Knowing where the money goes in a total hip replacement package helps patients and their families plan more effectively. In India, the total cost of hip replacement surgery, which is ₹3,00,000 to ₹5,00,000, covers every essential aspect of the treatment, from diagnosis to recovery support.
- In the initial phase, diagnostic tests including blood work, imaging scans, and pre-anesthesia clearance typically cost between ₹15,000 and ₹25,000. These are necessary to confirm the patient's surgical readiness.
- The surgical fees for the orthopedic surgeon and anesthetist range from ₹60,000 to ₹1,00,000, depending on the surgeon's experience and hospital reputation. It includes preoperative planning, surgery, and postoperative rounds.
- Implant cost makes up a significant portion of the total, ranging from ₹80,000 to ₹1,50,000. Ceramic and imported implants are usually at the higher end, while metal implants are more economical.
- Hospital charges, including room rent, operating theatre usage, nursing care, and consumables, typically fall between ₹1,00,000 and ₹1,50,000 for a 5–7 day stay in a private room.
- Medications, physiotherapy, and postoperative monitoring can cost another ₹30,000 to ₹60,000, depending on the patient's condition and the pace of recovery.
Cost Component | Estimated Cost (INR) |
| Pre-surgery Investigations | ₹15,000 – ₹25,000 |
| Surgeon & Anesthesia Fees | ₹60,000 – ₹1,00,000 |
| Hip Implant (metal/ceramic) | ₹80,000 – ₹1,50,000 |
| Hospital Stay & Surgery Charges | ₹1,00,000 – ₹1,50,000 |
| Medications & Post-op Care | ₹30,000 – ₹60,000 |
| Total Estimated Cost | ₹3,00,000 – ₹5,00,000 |
Note: The final cost of THR surgery may vary based on implant brand, complications, hospital location, and recovery needs.
How Does the Cost of Total Hip Replacement in India Compare with Other Countries?
India offers total hip replacement at a significantly lower price than many developed nations, while still delivering world-class outcomes. Patients from the US, UK, Europe, and the Middle East often choose India not only for the savings but also for the quality of care, faster scheduling, and personalized service.
The difference in cost can be as high as 70–80%, even when performed in internationally accredited hospitals by experienced orthopedic surgeons.
Country | Average Cost (USD) | What’s Included |
| India | $3,600 – $6,000 | Surgery, implant, hospital stay, anesthesia, meds, physiotherapy |
| United States | $30,000 – $50,000 | Often excludes implant cost and complete rehab; insurance co-pay may still apply |
| United Kingdom | $25,000 – $40,000 | Covered by NHS for residents; private cost is high |
| Canada | $28,000 – $45,000 | Long wait times in the public system; private care is costly for foreign nationals |
| UAE / Middle East | $20,000 – $35,000 | Premium services; high surgeon and facility charges |
| Singapore | $18,000 – $30,000 | High-quality care, but expensive due to service fees and hospital overhead |
| Thailand | $7,000 – $12,000 | Cheaper than West, but still more than India for equivalent quality |
What Factors Influence the Cost of Total Hip Replacement in India?
The total cost of hip replacement surgery in India ranges from $3,600 to $6,000, but this range can shift based on several key factors. Knowing these influences can help patients plan their treatment more effectively and avoid unexpected expenses.
- Type of Implant Used: The choice of implant is one of the most significant cost determinants. Metal-on-polyethylene implants are budget-friendly, while ceramic or imported titanium implants are more durable but expensive.
- Hospital Reputation and Location: Top-tier hospitals in metro areas like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore may charge more due to their advanced surgical infrastructure and internationally trained surgeons.
- Surgeon's Experience: Highly experienced orthopedic surgeons, especially those trained internationally or who specialize in joint replacement, may have higher surgical fees.
- Type of Surgery (Unilateral or Bilateral): Replacing both hips (bilateral) in a single or staged surgery increases the overall cost. A unilateral hip replacement is less expensive and takes less time to recover.
- Surgical Technique Used: Minimally invasive techniques may increase costs slightly due to the need for specialized instruments and higher surgeon skill.
- Duration of Hospital Stay: A typical stay is 5 to 7 days. If the patient has comorbidities like diabetes, heart disease, or post-op complications like infection or delayed mobility, the stay may extend, adding to the cost.
- Postoperative Medications and Physiotherapy: Recovery requires pain management, antibiotics, and rehabilitation. The longer the recovery phase or the more intensive the therapy needed, the higher the expenses.
Why Do International Patients Prefer India for Total Hip Replacement?
- Affordable World-Class Care: India offers high-quality hip replacement surgery at a fraction of the cost charged in Western countries, without compromising medical standards or safety.
- Globally Trained Orthopedic Surgeons: Indian surgeons are highly skilled, with many having received training in the UK, USA, or Europe. Their experience in high-volume joint centers ensures precision and better outcomes.
- Advanced Hospitals with Modern Infrastructure: Internationally accredited hospitals in India are equipped with modular operating rooms, infection control systems, and advanced implants.
- No Waiting List for Surgery: Unlike public healthcare systems abroad, Indian hospitals schedule surgeries quickly, which is critical for patients dealing with severe pain or mobility issues.
- Complete International Patient Support: From visa assistance and airport pick-up to translation services and follow-up coordination, Indian hospitals provide end-to-end support for foreign patients.
- Vast Implant Choices at Regulated Prices: Patients can choose from various implant brands, including imported options, all priced transparently and regulated by Indian health authorities.
- Excellent Recovery and Physiotherapy Services: Dedicated rehabilitation teams help THR patients regain strength and mobility more quickly with structured physiotherapy, available both inpatient and outpatient.
What Is the Success Rate and Recovery Timeline After a Total Hip Replacement in India?
Total hip replacement surgery in India has shown consistently excellent results, both in terms of pain relief and functional recovery. With modern surgical techniques, high-quality implants, and structured rehabilitation, most patients regain mobility and return to daily activities within a few months.
Success Rate of Total Hip Replacement in India
The success rate of total hip replacement surgery in India ranges from 95% to 98%, primarily when performed in experienced orthopedic centers using quality implants. Patients typically report:
- Pain relief in the first few weeks
- Improved range of motion and walking ability within 1 to 2 months
- Long-lasting results, with implants functioning well for 15–25 years or more
Success is measured not only by the absence of complications but also by how well patients return to independent living and enjoy improved quality of life. India's top joint replacement centers adhere to evidence-based protocols that minimize infection risks, reduce hospital stays, and expedite recovery.
Factors that contribute to the high success rate in India include:
- Use of advanced surgical techniques, such as robotic, minimally invasive, and muscle-sparing approaches
- Strict sterility standards in modular operating theatres
- Surgeon experience, especially in handling complex or revision cases
- Strong focus on early mobilization and rehabilitation
Recovery Timeline After Hip Replacement Surgery
Recovery after total hip replacement occurs in phases, and although every patient heals at a different pace, most follow a predictable path.
- Hospital Stay (5 to 7 Days): Patients are usually encouraged to sit up and begin walking with support within 24 to 48 hours after THR surgery. Physiotherapists assist with gentle exercises and gait training during this time. Pain is managed with medications, and the surgical wound is monitored for signs of healing.
- Initial Home Recovery (Week 1 to Week 4): After discharge, patients continue exercises at home or in a hotel-apartment setup near the hospital (for international patients). Movement improves steadily, but walking aids, such as a walker or cane, are usually needed. Swelling, mild pain, or stiffness are normal during this phase.
- Strength and Stability Phase (Weeks 4-8): By 4 to 6 weeks, most patients can walk independently and begin performing light activities, such as climbing stairs or taking short walks outdoors. Physiotherapy may shift to more strength-focused routines. Many patients return to desk jobs or low-impact work by the end of this period.
- Long-Term recovery (3 to 6 Months): Full recovery and return to regular daily routines, including driving, traveling, and recreational walking, typically occur within 3 to 6 months. With high-quality implants and proper care, patients can resume active lifestyles without pain or limitation. Heavy lifting, running, or participating in high-impact sports may be restricted to prevent early wear and tear on the joint.
- Implant Longevity and Maintenance (After 6 Months): Modern hip implants in India typically last 15 to 25 years or longer, especially when using ceramic or titanium components. Patients are advised to avoid smoking, maintain a healthy weight, and follow up annually to monitor joint health through X-rays or check-ups.
Note: Recovery speed depends on the patient's age, preoperative fitness, weight, and whether the surgery was unilateral or bilateral. Patients with other health issues like diabetes or osteoporosis may need additional time and supervision.
Total Hip Replacement - THR Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Total Hip Replacement - THR costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $3,600 - $6,000 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
Leading Hospitals for Total Hip Replacement - THR in India

SP Medifort Hospital
SP Medifort, Thiruvananthapuram, is a JCI-accredited, 475-bed multi-super-specialty hospital spread across 500,000 sq. ft. The hospital houses 10 modu...
Accreditations


Facilities

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, is a 435-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital with 120 critical care beds. Established in 20...
Accreditations

Facilities

AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, is a 1,000-bed, JCI- and NABH-accredited super-specialty hospital spanning 1.7 million sq. ft. It is the flagshi...
Accreditations


Facilities

Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai
Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai, is a 200-bed quaternary-care hospital and part of the IHH Healthcare network, one of the world’s largest priva...
Accreditations

Facilities

MGM Healthcare, Chennai
MGM Healthcare, Chennai, is a 400-bed quaternary-care super-specialty hospital accredited by JCI, NABH, and NABL. The hospital features 100 ICU beds,...
Accreditations


Facilities

MIOT International, Chennai
MIOT International, Chennai, is a 1,000-bed NABH- and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital serving patients from more than 130 countries. Establish...
Accreditations

Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai, is the flagship hospital of the Apollo Group. Established in 1983, it has 560 beds, 46 ICUs, and 15 operating...
Accreditations



Facilities

HCG Cancer Centre, Mumbai
HCG Cancer Centre, Borivali, Mumbai, is an NABH- and AACI-accredited comprehensive cancer hospital established in 2019. The 119-bedded facility includ...
Accreditations


Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, established in 2016, is a 500-bed JCI- and NABH-accredited quaternary care hospital offering advanced treatment across...
Accreditations


Facilities

Marengo Asia Hospitals, Faridabad
Marengo Asia Hospital, formerly QRG Health City, is a 325-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital in Faridabad. It offers advanced care i...
Accreditations

Facilities
FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Related Procedures
Other procedures in this department
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
