Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion - TLIF Surgery Cost in India
About Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion - TLIF Surgery
What Is TLIF Surgery and Why Is It Done?
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is a spinal fusion surgery used to stabilize the lower (lumbar) spine. It is primarily advised for patients suffering from chronic back pain, leg pain (sciatica), or spinal instability due to conditions such as degenerative disc disease, spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis, or recurrent disc herniation.
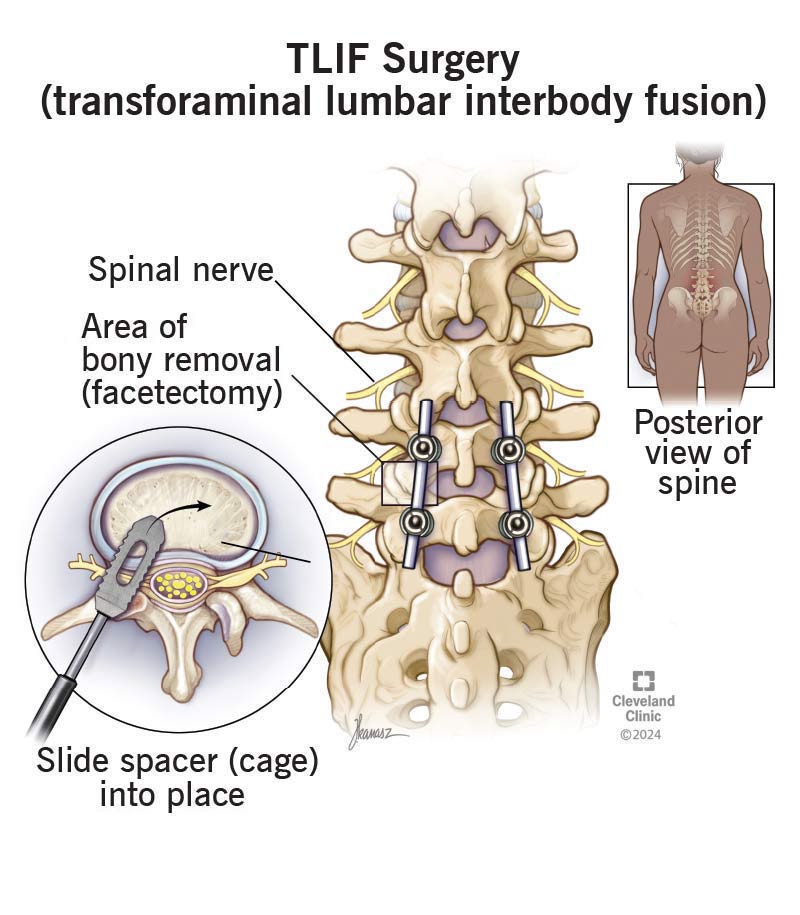
In TLIF, the surgeon approaches the spine through the side of the vertebra (transforaminal route), removes the damaged intervertebral disc, and places a bone graft or cage between the two vertebrae. Over time, the vertebrae fuse into a single, solid bone. The fusion eliminates painful motion at the joint and restores stability to the spine.
TLIF is chosen over other fusion methods because:
- It allows access to both sides of the disc space through a single incision.
- It minimizes manipulation of the spinal cord and nerves.
- It provides better alignment and load-bearing capability for the spine.
- It can be performed as an open or minimally invasive procedure, depending on the case.
The goal of TLIF is to relieve nerve compression, reduce pain, and restore spine function by stabilizing the affected vertebral segment. It is often considered when conservative treatments such as medications, physical therapy, or epidural injections have failed.
Who Needs TLIF Surgery?
TLIF surgery is recommended for patients who experience persistent lower back pain, radiating leg pain, or spinal instability that does not improve with non-surgical treatments. It is particularly suited for individuals with structural problems in the lumbar spine that involve disc degeneration or vertebral slippage, leading to compression of the spinal nerves.
Some of the most common conditions that indicate the need for TLIF are:
- Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD): When the intervertebral discs lose hydration and height due to aging or wear and tear, they may collapse and cause painful friction between the vertebrae. TLIF restores disc height and stabilizes the segment.
- Spondylolisthesis: This disease occurs when one vertebra slips forward over the one below it. TLIF prevents further slippage by fusing the unstable segment and relieving nerve compression.
- Lumbar Disc Herniation (with Recurrent Symptoms): In cases where disc herniation causes severe leg pain (sciatica) and returns after a discectomy or other procedures, TLIF is used to permanently stabilize the affected level.
- Spinal stenosis (with instability): When narrowing of the spinal canal compresses nerves and is accompanied by unstable motion, TLIF helps decompress the nerves and fuse the spine to prevent further damage.
- Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS): Patients who continue to have pain after previous spinal procedures may benefit from TLIF if imaging shows instability, non-union, or recurring disc issues.
- Spinal Fractures or Infections: In select cases of traumatic injury or infection that compromise spinal stability, TLIF may be used to reconstruct and fuse the spine.
TLIF is typically considered only after non-surgical treatments such as rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or epidural steroid injections have failed for 6-12 weeks or longer. It is suitable for adults of various ages, but especially common in those between 35 and 70 years experiencing nerve-related back and leg pain.
How Is TLIF Surgery Performed?
Surgeons perform transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) to take out a damaged disc in the lower spine and fuse two vertebrae for permanent stability. The entire surgery typically takes 2 to 4 hours and is carried out under general anesthesia. The surgery involves several steps.
- Positioning and Preparation: The surgical team positions the patient face-down on a padded operating table. Once under anesthesia, the surgeon cleans and sterilizes the lower back and marks the entry point over the affected vertebral level.
- Making the Incision: The surgeon makes a small incision along the midline or side of the lower back. In minimally invasive TLIF, this incision is only 2-4 cm, while open surgery requires a slightly larger cut.
- Accessing the Spine and Removing Bone: To reach the disc space, the surgeon gently retracts the muscles and exposes the vertebrae. They may remove part of the facet joint or lamina to visualize the nerve roots and disc clearly.
- Disc Removal and Nerve Decompression: The surgeon carefully removes the damaged disc between the two vertebrae. Any bone spurs or soft tissues compressing the nerves are also cleared to relieve pressure on spinal nerves.
- Implanting the Spacer or Cage: After cleaning the disc space, the surgeon inserts a bone graft-filled spacer or cage between the vertebrae. It restores disc height and promotes bone growth. The cage may be made of PEEK, titanium, or carbon fiber.
- Placing Screws and Rods: To stabilize the spine, the surgeon inserts pedicle screws and rods into the vertebrae above and below the disc space. These implants hold the bones in place while fusion occurs.
- Closure and Dressing: Once the implants are secured and alignment confirmed, the surgeon closes the incision in layers using sutures. Spine surgeons apply a sterile dressing to prevent infection.
- Post-Surgery Monitoring: The patient is shifted to a recovery room and monitored for vital signs and neurological function. Pain management begins immediately, and walking is encouraged within 24-48 hours.
Many hospitals now offer minimally invasive TLIF (MIS-TLIF), which reduces muscle damage, blood loss, and hospital stay. The choice between open and MIS depends on the patient’s anatomy, diagnosis, and the surgeon’s preference.
Send Query
About Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion - TLIF Surgery in India
What is the Cost of TLIF Surgery in India?
The cost of TLIF surgery in India typically ranges from $5,000 to $8,500, depending on the number of spinal levels involved, the type of implants used, and the hospital’s facilities. This cost is significantly lower than in the US, UK, or Australia, where the same procedure may exceed $30,000 to $60,000.
What sets India apart is not just affordability, but the comprehensive nature of TLIF surgery packages. Hospitals offer all-inclusive pricing with no hidden charges, covering every step of the treatment journey, from pre-surgery consultations to rehabilitation.
TLIF surgery cost in India generally includes:
- Pre-Operative Evaluation: It includes MRI scans, X-rays, CT scans, blood tests, ECG, and anesthesia fitness assessment required for planning and safety.
- Surgeon’s and Anesthetist’s Fees: The total cost includes professional fees for the neurosurgeon or orthopedic spine specialist, the assisting surgical team, and the anesthesiologist.
- Operation Theatre Charges and Surgical Tools: It covers sterile instruments, neuromonitoring systems, fluoroscopy, and high-precision surgical equipment needed during the procedure.
- Spinal Implants and Cage System: Premium hospitals use FDA- or CE-approved spinal implants, including pedicle screws, titanium rods, and interbody cages. The implant cost is a significant portion of the total expense.
- Hospital Stay and ICU Monitoring: Patients usually stay in the hospital for 4 to 7 days, including 1 day in the ICU (if required). It includes nursing care, room charges, and monitoring.
- Inpatient Medications and Consumables: It includes IV antibiotics, painkillers, dressings, surgical sutures, and disposables used during the hospital stay.
- Physiotherapy and Mobilization Support: Basic post-surgical rehabilitation, including walking training, mobility support, and exercise guidance, is part of the standard package.
- Post-Discharge Follow-Up: Many hospitals include one or two follow-up consultations, wound inspections, and X-rays after discharge to monitor recovery.
In short, TLIF spine surgery in India offers not only significant cost savings but also a well-structured, end-to-end treatment plan that meets global standards.
Breakdown of TLIF Surgery Cost in India
The total cost of TLIF (transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion) surgery in India is influenced by several components, each contributing to the final package. Understanding this breakdown helps international patients prepare better and ensures transparency.
- The pre-operative evaluation for TLIF in India, including MRI, X-ray, blood tests, and anesthesia fitness, typically costs $300 to $600, depending on the diagnostic complexity.
- The TLIF implant cost, which includes titanium or PEEK cages, pedicle screws, and rods, ranges from $1,800 to $3,000. Hospitals use globally approved implants from brands like Medtronic, Stryker, or Zimmer Biomet.
- Surgeon’s and anesthetist’s fees are usually between $1,000 - $1,500, depending on the surgeon’s seniority and the surgical duration.
- Operation theatre charges, including advanced equipment (fluoroscopy, neuromonitoring, C-arm), generally fall in the range of $700 to $1,000.
- The hospital stay for TLIF in India, including 1 day ICU and 4-6 days in a private room, costs around $800 to $1,200, inclusive of nursing and meals.
- Inpatient medications and surgical consumables, such as antibiotics, painkillers, drapes, and sutures, add another $300 to $500 to the bill.
- Post-operative physiotherapy and mobilization, provided during the hospital stay, may cost $100 to $200, depending on the number of sessions.
Cost Component | Estimated Cost (USD) |
| Pre-operative Investigations | $300 – $600 |
| Spinal Implants and Hardware | $1,800 – $3,000 |
| Surgeon and Anesthetist Fees | $1,000 – $1,500 |
| Operation Theatre and Equipment | $700 – $1,000 |
| Hospital Stay and Nursing Care | $800 – $1,200 |
| Medications and Surgical Supplies | $300 – $500 |
| In-Hospital Physiotherapy | $100 – $200 |
| Total Estimated Cost (Single-Level TLIF) | $5,000 – $8,500 |
Note: This pricing applies to single-level TLIF surgery. In cases where multi-level fusion or additional spinal instrumentation is required, the cost may increase proportionally due to extended operating time, extra implants, and longer hospital stay.
Cost Comparison: TLIF Surgery in India vs Other Countries
TLIF surgery in India offers exceptional value compared to the same procedure in countries like the USA, UK, Australia, or the UAE. International patients often save up to 70–80% by choosing India, while still receiving globally approved implants, expert spine surgeons, and modern hospital facilities.
Country | Average TLIF Cost (USD) | Inclusions and Remarks |
| India | $5,000 – $8,500 | All-inclusive; covers surgery, implants, stay, meds, and physiotherapy |
| United States | $35,000 – $60,000 | Excludes rehab and extended hospital stay; costs vary widely by state |
| United Kingdom | $25,000 – $45,000 (Private) | NHS wait times; private care is expensive and not always fully inclusive |
| Australia | $28,000 – $50,000 | Partial insurance coverage; extra cost for implants and rehab |
| UAE | $18,000 – $25,000 | Premium pricing for private care; limited minimally invasive options |
| Singapore | $20,000 – $35,000 | High-tech hospitals but costly; post-op physiotherapy is often billed separately |
| Thailand | $8,500 – $12,000 | Cheaper than Western countries but still 30–50% higher than India |
With skilled spine surgeons, high success rates, and all-inclusive cost transparency, India remains one of the top choices for affordable TLIF surgery worldwide.
What Factors Influence TLIF Surgery Cost in India?
Several medical, surgical, and logistical factors influence the final cost of TLIF surgery in India. These variables help determine whether the patient’s treatment falls at the lower or higher end of the cost range.
- Number of Spinal Levels Fused: Single-level TLIF is more affordable. If multiple levels (e.g., L4-L5 and L5-S1) need to be fused, the cost increases due to additional implants, longer surgical time, and extended hospital stay.
- Type and Brand of Implants Used: The choice of cage (PEEK or titanium), pedicle screws, rods, and the brand of implants significantly impacts the cost. Premium brands like Medtronic, Globus, Stryker, and Zimmer Biomet cost more but offer superior durability and compatibility.
- Surgical Technique (Open vs. Minimally Invasive): Minimally Invasive TLIF (MIS-TLIF) uses specialized tools, smaller incisions, and advanced imaging. It leads to faster recovery and less blood loss, but may raise the overall cost due to equipment and technical expertise.
- Hospital Category and Location: Hospitals in metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore, especially those with JCI or NABH accreditation, may charge more than smaller-tier city hospitals due to their superior infrastructure and international services.
- Surgeon’s Experience and Specialty: Highly experienced spine surgeons with fellowship training and specialization in complex fusions or revisions may charge higher professional fees, but often result in better outcomes and fewer complications.
- Pre-Existing Medical Conditions: If the patient has comorbidities like diabetes, obesity, or heart disease, they may require additional monitoring, ICU support, or extended stay, all of which increase the total bill.
- Post-Operative Rehabilitation Needs: Extended physiotherapy, advanced mobility aids (e.g., spinal braces, walking frames), and longer rehab stays can add to the cost. Some patients may also require follow-up imaging or pain management sessions.
- Accommodation and International Patient Services: Foreign patients may require visa assistance, airport transfers, interpreters, and arrangements for attendants to stay. These services are sometimes bundled into the package or billed separately.
Why Is TLIF Surgery More Affordable in India?
India offers world-class spine surgery at a fraction of the cost seen in other developed countries, without compromising on surgical quality, implant standards, or patient outcomes. The affordability of TLIF surgery in India stems from a combination of healthcare system efficiencies, lower operational costs, and patient-centered package models.
Some of the key reasons why TLIF surgery is more cost-effective in India are:
- Lower Operational and Infrastructure Costs: Indian hospitals operate at significantly lower costs for equipment maintenance, utilities, and staffing. These savings are passed directly to patients through reduced surgical pricing.
- Affordable Surgeon and Staff Fees: Highly skilled spine surgeons in India, many of whom have trained internationally, charge significantly less than their counterparts in the US or UK. Anesthetists, nurses, and physiotherapists also receive modest salaries, which helps keep overall costs low.
- Competitive Implant Pricing: India has access to a broad range of spinal implants, including both locally manufactured and globally imported options. With reduced import taxes and bulk procurement, hospitals can offer FDA/CE-approved implants at affordable rates.
- High Patient Volume and Streamlined Processes: Spine centers in India handle a large number of TLIF and other fusion surgeries annually. It allows hospitals to optimize surgical time, reduce inventory waste, and lower per-patient costs through volume efficiency.
- Integrated In-House Services: Hospitals offer diagnostics, pharmacy, physiotherapy, and rehab services on-site, eliminating the need for third-party outsourcing. It improves care continuity and significantly reduces overhead costs.
- Transparent and All-Inclusive Packages: Unlike Western countries, where patients are billed separately for consultation, surgery, implants, stay, and rehab, Indian hospitals bundle these into fixed-cost packages, ensuring price clarity and avoiding hidden expenses.
- Favorable Currency Exchange for International Patients: Patients traveling from countries like the USA, UK, UAE, Canada, or Africa benefit from favorable exchange rates, making high-end spine treatment in India far more affordable than in their home countries.
- Government Support for Medical Tourism: India promotes medical tourism with easy visa processes, airport assistance, multilingual support, and dedicated international patient departments in major hospitals.
International Patient Services for TLIF Surgery in India
India’s top hospitals provide a complete range of international patient services tailored to make spinal treatments like TLIF surgery smooth, safe, and stress-free for patients arriving from abroad. These services are often bundled with the treatment package or offered at minimal additional cost, ensuring convenience from pre-travel planning to post-surgery recovery.
- Medical Visa Assistance: Hospitals issue official medical invitation letters required for visa applications. International patient coordinators guide patients and their companions through the process and also assist with visa extensions when necessary.
- Airport Pickup and Drop Services: Patients are received at the airport by a hospital-appointed representative and transported safely to their accommodation or directly to the hospital. Return airport transfers are also arranged post-recovery.
- Dedicated International Patient Coordinator: Each patient is assigned a case manager who handles daily scheduling, interpreter services, billing support, travel assistance, and coordination with the surgical team.
- Multilingual Interpretation Services: To eliminate language barriers, interpreters are provided for Arabic, Russian, French, Spanish, Swahili, and more. Essential documents and medical reports are translated upon request.
- Pre-Travel Online Consultation: Patients can book an online video consultation with a spine surgeon before flying. It allows the doctor to review reports, explain the TLIF procedure, and provide a personalized estimate and treatment plan.
- Affordable Accommodation and Meal Options: Hospitals assist in booking budget hotels, guesthouses, or service apartments near the hospital. Meal plans are customizable and include halal, vegetarian, and diabetic-friendly options based on patient preference.
- Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy Support: After TLIF surgery, in-house physiotherapists provide mobilization training, posture correction, and spine-strengthening exercises. Customized rehab plans are shared for continued recovery after the patient returns home.
- Post-Discharge Remote Follow-Up: Surgeons remain available for virtual follow-ups via video, email, or WhatsApp. Patients can send updates, X-rays, or queries for months after returning home, at no extra charge.
- Assistance with FRRO Registration: For extended stays in India, hospitals help international patients complete FRRO (Foreigner Regional Registration Office) formalities to remain compliant with local laws.
- Family Support and Recovery Comfort: Hospitals offer companion support, including extra bedding, visitor access, and meal services for relatives. Recovery lounges and spiritual spaces are also available for patient comfort.
What is the Success Rate and Recovery Timeline After TLIF Surgery in India?
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion surgery is a highly successful spinal procedure, primarily when performed by experienced surgeons using high-quality implants. It is designed to relieve chronic lower back and leg pain, restore spinal stability, and improve mobility. In India, the procedure has shown excellent clinical outcomes, even in complex or revision cases.
Success Rate of TLIF Surgery in India
- The average success rate of TLIF surgery in India is around 90% to 95% for single-level fusion, depending on patient condition, surgeon experience, and surgical technique (open vs minimally invasive).
- Most TLIF patients report a significant reduction in pain and improved quality of life within 3 to 6 months of the procedure.
- Minimally Invasive TLIF often results in faster healing, reduced post-op pain, and shorter hospital stays, contributing to better patient satisfaction.
- Complication rates are relatively low in India due to advanced intraoperative technologies such as intraoperative neuromonitoring, C-arm navigation, and modern fusion systems.
Recovery Timeline After TLIF Surgery
Recovery after TLIF is gradual and can vary based on factors like the number of spinal levels fused, patient age, comorbidities, and whether the surgery was open or minimally invasive.
- Day 1-2: Patient is monitored in the hospital (1 day in ICU if needed). Pain is managed through IV medications. Breathing and leg movement exercises begin early.
- Day 3-5: Patient is encouraged to walk with support. Light physiotherapy begins. If stable, discharge is possible by day 4 or 5.
- Week 2-3: Staples or sutures are removed. The patient continues basic home-based physiotherapy. Bending and lifting are avoided.
- Week 4-6: Patient gains more mobility. Can walk longer distances and perform light tasks. Follow-up imaging may be scheduled.
- Month 3-6: Fusion progresses. Pain reduces significantly. Return to desk work or non-strenuous job roles is often possible.
- 6-12 Months: Bone graft fully fuses with the vertebrae. The patient can resume most normal activities, including travel, long walks, or non-impact exercise. Complete recovery usually occurs within 12 months.
Post-Operative Do’s and Don’ts
- Do follow a supervised physiotherapy plan. It’s essential for regaining strength and spine mobility.
- Don’t lift heavy objects or bend forward until your surgeon gives clearance.
- Do attend all follow-up visits and get periodic imaging (X-ray/CT) to monitor fusion progress.
- Don’t ignore numbness or new leg pain, which may indicate nerve irritation.
Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion - TLIF Surgery Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion - TLIF Surgery costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $5,000 - $8,500 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
Leading Hospitals for Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion - TLIF Surgery in India

SP Medifort Hospital
SP Medifort, Thiruvananthapuram, is a JCI-accredited, 475-bed multi-super-specialty hospital spread across 500,000 sq. ft. The hospital houses 10 modu...
Accreditations


Facilities

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, is a 435-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital with 120 critical care beds. Established in 20...
Accreditations

Facilities

AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, is a 1,000-bed, JCI- and NABH-accredited super-specialty hospital spanning 1.7 million sq. ft. It is the flagshi...
Accreditations


Facilities

Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai
Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai, is a 200-bed quaternary-care hospital and part of the IHH Healthcare network, one of the world’s largest priva...
Accreditations

Facilities

MGM Healthcare, Chennai
MGM Healthcare, Chennai, is a 400-bed quaternary-care super-specialty hospital accredited by JCI, NABH, and NABL. The hospital features 100 ICU beds,...
Accreditations


Facilities

MIOT International, Chennai
MIOT International, Chennai, is a 1,000-bed NABH- and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital serving patients from more than 130 countries. Establish...
Accreditations

Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai, is the flagship hospital of the Apollo Group. Established in 1983, it has 560 beds, 46 ICUs, and 15 operating...
Accreditations



Facilities

HCG Cancer Centre, Mumbai
HCG Cancer Centre, Borivali, Mumbai, is an NABH- and AACI-accredited comprehensive cancer hospital established in 2019. The 119-bedded facility includ...
Accreditations


Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, established in 2016, is a 500-bed JCI- and NABH-accredited quaternary care hospital offering advanced treatment across...
Accreditations


Facilities

Marengo Asia Hospitals, Faridabad
Marengo Asia Hospital, formerly QRG Health City, is a 325-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital in Faridabad. It offers advanced care i...
Accreditations

Facilities
Gallery

FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Related Procedures
Other procedures in this department
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
