Bone Marrow Transplant - BMT Cost in India
About Bone Marrow Transplant - BMT
What Is a Bone Marrow Transplant?
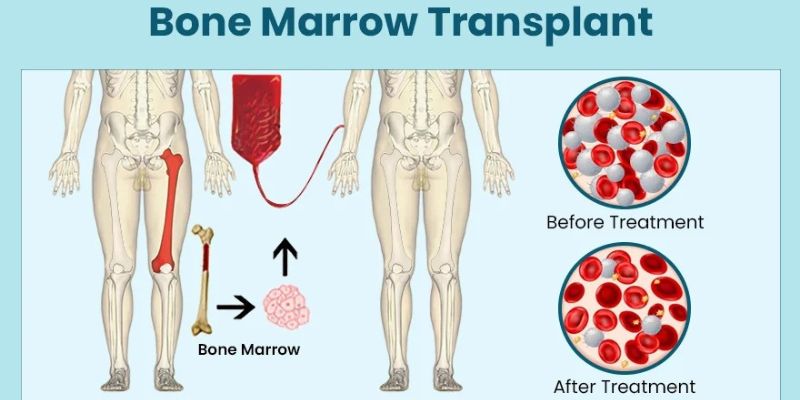
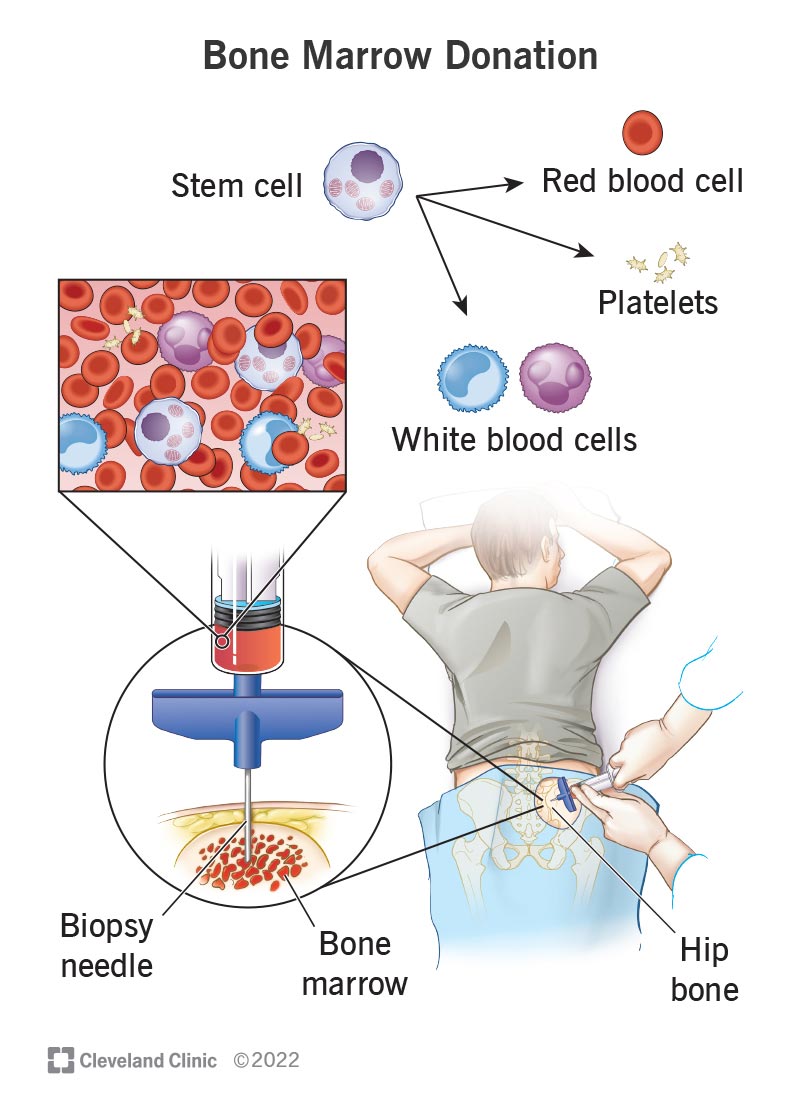
A bone marrow transplant, abbreviated as BMT, is a medical treatment that replaces unhealthy or damaged bone marrow with healthy blood-forming stem cells. Marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside our bones. It works like a factory, producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets (the essential components of blood).
When the bone marrow stops functioning properly (either due to diseases such as blood cancer, genetic conditions, or certain infections), it can no longer make healthy blood cells. That's when a bone marrow transplant becomes necessary.
How Does It Work?
The transplant process involves first removing the unhealthy or cancerous cells in the bone marrow using chemotherapy or radiation. Once the body is ready, healthy stem cells are infused into the bloodstream. These new cells travel to the bone marrow spaces and begin creating fresh, healthy blood cells (a process called engraftment).
Think of it as restarting your body's blood-making system, similar to resetting a computer to fix a deep error.
Why Are Stem Cells So Important?
Stem cells are special cells that can develop into any blood cell your body needs. In BMT, we use these stem cells to rebuild a healthy blood and immune system. Without enough working stem cells, the body cannot fight infections, carry oxygen, or stop bleeding.
Where Do These Stem Cells Come From?
Stem cells used in bone marrow transplants can come from different sources:
- Your own body (autologous transplant): In some cases, stem cells are collected from your own blood before chemotherapy and given back after treatment.
- A donor (allogeneic transplant): For certain diseases, the best option is to use stem cells from a healthy donor. It could be a sibling, a matched unrelated donor, or even a half-matched family member.
- Umbilical cord blood: In exceptional cases, stem cells may come from donated cord blood collected at birth.
What Makes Matching Important?
In donor-based transplants (allogeneic BMT), HLA matching is key. HLA, or Human Leukocyte Antigen, is a genetic marker used to match donors and recipients for transplantation purposes. A closer match means fewer complications and a better chance of success.
Why Is Bone Marrow Transplant Needed?
A bone marrow transplant is not something people need on a daily basis. It's a major treatment usually recommended when a person's bone marrow is no longer able to make healthy blood cells or when the blood cells themselves are abnormal. It can occur due to certain blood cancers, genetic diseases, or bone marrow failure.
Below are the most common conditions where a BMT can be life-saving or life-changing.
- Leukemia is a type of blood cancer where the marrow produces abnormal white blood cells that grow uncontrollably and crowd out healthy cells. A bone marrow transplant can replace the cancer-filled marrow with new, healthy stem cells, helping the patient recover and stay cancer-free.
- Lymphoma affects the lymphatic system, a component of the immune system. In aggressive or relapsed cases of lymphoma, especially Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, BMT is used to rebuild the immune system after intensive chemotherapy.
- Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects the plasma cells. In many patients, an autologous transplant (using the patient's own stem cells) helps control the disease and extend survival.
- Aplastic anemia is a condition in which the marrow stops producing enough blood cells altogether. It can be caused by the body's immune system attacking the marrow, certain medications, or unknown reasons. A donor transplant (allogeneic BMT) can replace the non-functioning marrow with healthy stem cells.
- Thalassemia is a genetic blood disorder in which the body is unable to produce normal hemoglobin, leading to severe anemia. Children with thalassemia often need regular blood transfusions. A BMT is the only known cure for this condition, especially in younger patients.
- Sickle cell disease is an inherited condition that causes RBCs to become misshapen (sickle-shaped), resulting in blockages, pain, and organ damage. A successful BMT can cure sickle cell disease by providing the patient with new stem cells that produce normal-shaped red blood cells.
- Rare inherited conditions (such as Fanconi anemia, SCID (Severe Combined Immunodeficiency), and certain metabolic or immune system disorders) can also be treated or cured through a bone marrow transplant, especially if done early in life.
What Are the Different Bone Marrow Transplant Types?
Doctors choose the type of bone marrow transplant based on the patient's disease, age, overall health, and the availability of a suitable donor. Each type uses healthy stem cells, but their source may vary.
Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant
In an autologous transplant, doctors collect and preserve the patient's own stem cells before starting high-dose chemotherapy or radiation. Once the treatment ends, they reinfuse the stem cells to help the body recover. Autologous BMT is commonly used for cancers such as lymphoma and multiple myeloma, where the patient's own bone marrow remains healthy and viable.
- Key Advantage: The patient's body is less likely to reject the stem cells since they come from the same person.
- Limitation: If any cancer cells remain in the collected stem cells, they may cause relapse.
Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant
An allogeneic transplant uses stem cells from another person, usually a sibling, relative, or unrelated matched donor. Allogeneic BMT is essential for treating genetic disorders, leukemia, and bone marrow failure syndromes. The new stem cells create a healthy blood system and may also attack remaining cancer cells (a process called graft-versus-tumor effect).
- Key Advantage: Donor stem cells can completely replace the damaged immune system and more effectively eliminate cancer.
- Limitation: The body may reject the new cells or develop graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), in which donor cells attack the recipient's tissues.
Haploidentical Bone Marrow Transplant
When a perfect donor match isn't available, doctors consider a haploidentical transplant. In haploidentical BMT, the donor shares only half of the genetic markers (usually a parent, sibling, or child). Newer techniques and drugs now make this option safer and more effective.
- Key Advantage: A suitable donor is easier to find within the family, even if the match isn't perfect.
- Limitation: The risk of complications like GVHD can be higher, though modern medical care can reduce this.
Umbilical Cord Blood Transplant
Doctors can also use stem cells collected from a newborn's umbilical cord and placenta. These stem cells are stored in cord blood banks and don't require a perfect match because they are very adaptable.
- Key Advantage: Cord blood transplants offer more flexibility with donor matching.
- Limitation: The number of stem cells in a single cord blood unit may not be adequate for adults, resulting in a longer recovery time.
Step-by-Step Bone Marrow Transplant Procedure
Understanding each stage of the bone marrow transplant process helps patients and their families prepare better, both emotionally and physically. Here's a clear overview of what happens from the first consultation to the recovery phase.
Pre-Transplant Evaluation and Planning
Doctors begin with a complete medical evaluation. It includes blood tests, imaging scans, heart and lung function tests, and a bone marrow biopsy. They assess whether the patient is fit for transplant and determine the most suitable type. Patients also meet with transplant coordinators, dietitians, and psychologists to understand the procedure, potential side effects, and the emotional impact of the treatment.
Stem Cell Collection
If the transplant is autologous, doctors collect the patient's stem cells using a process called apheresis. The patient receives injections over a few days to stimulate stem cell production. Doctors draw blood, pass it through a machine that separates stem cells, and return it to the body. For allogeneic BMT, stem cells are collected from the matched donor using the same method. Alternatively, bone marrow may be directly extracted from the donor's hip bone under anesthesia.
Conditioning Treatment (Chemotherapy/Radiation)
Once stem cells are collected, the patient receives high-dose chemotherapy, sometimes combined with radiation. The conditioning phase removes cancer cells and suppresses the immune system, allowing the new stem cells to settle in. While this stage is aggressive, it plays a key role in clearing out damaged or diseased cells.
Transplantation Day (Infusion of Stem Cells)
After conditioning, doctors infuse the healthy stem cells through an intravenous (IV) line. The process is similar to a blood transfusion. This is known as "Day 0." It's a simple, painless process that typically takes a few hours. The new stem cells travel through the bloodstream to the bone marrow, where these cells start producing healthy blood cells.
Engraftment and Monitoring
Engraftment is the process by which transplanted stem cells begin to produce new blood cells. It typically takes 10 to 28 days. During this period, the patient stays in a sterile transplant unit to reduce infection risk. Blood counts are monitored daily, and supportive care (antibiotics, antifungals, fluids, nutrition) is provided to manage side effects.
Recovery and Follow-Up
After successful engraftment, patients are gradually discharged. However, follow-up visits remain essential for the next 6 to 12 months. Doctors monitor organ function, blood counts, immune recovery, and potential complications, such as infections or graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Patients receive vaccinations and medications to support immune rebuilding.
Send Query
About Bone Marrow Transplant - BMT in India
What is the Cost of a Bone Marrow Transplant in India?
The bone marrow transplant cost in India ranges from ₹18,00,000 to ₹35,00,000 (approximately $21,600 to $42,000). The pricing depends on the type of transplant (autologous or allogeneic), the hospital's location, the patient's medical condition, and whether a donor is involved.
India offers a complete transplant package at an affordable rate without compromising on quality or safety. Many top-tier hospitals in India are internationally accredited and led by highly experienced hematologists and transplant surgeons. These centers utilize cutting-edge technology and adhere to global treatment protocols, making India a preferred destination for patients worldwide.
What's Included in the Cost?
The quoted bone marrow transplant cost in India usually includes:
- Doctor's consultation and surgeon's fee
- Hospital stay and nursing charges
- ICU and isolation room charges
- Pre-transplant investigations and diagnostics
- Cost of chemotherapy or radiation (conditioning therapy)
- Donor screening and matching (for allogeneic transplant)
- Bone marrow harvesting procedure
- Stem cell infusion procedure
- Medications during hospitalization
- Post-transplant monitoring during stay
- Short-term follow-up consultations
However, extended hospital stays, additional infections, or unexpected complications may increase the total cost. Long-term follow-up medications and outpatient visits after discharge are typically billed separately, unless they are part of a bundled package.
Cost Breakdown of Bone Marrow Transplant in India
The cost of a bone marrow transplant procedure in India depends on several critical components, including the type of transplant, pre-transplant evaluation, donor matching, ICU care, hospital stay, medications, and follow-up treatment.
- Pre-Transplant Evaluation Cost: Before the transplant is scheduled, doctors conduct several tests, including complete blood counts, bone marrow biopsies, imaging (such as CT/PET scans), cardiac evaluations, and specialist consultations. The pre-transplant diagnostic workup costs between ₹75,000 and ₹1,50,000 ($900 to $1,800).
- Donor Matching and HLA Typing Cost: For allogeneic and haploidentical transplants, finding a compatible donor is crucial. It involves high-resolution HLA typing. The cost of HLA typing and donor screening ranges from ₹60,000 to ₹1,20,000 ($720 to $1,450).
- Bone Marrow Transplant Surgery Cost: The transplant procedure itself involves the conditioning regimen (chemotherapy or radiation), stem cell infusion, and several weeks of intensive care. It is the most expensive part of the treatment. The surgery cost varies by type:
- Autologous transplant (using patient's own stem cells): ₹12 lakhs to ₹15 lakhs ($14,500 to $18,000)
- Allogeneic transplant (matched donor): ₹18 lakhs to ₹25 lakhs ($21,600 to $30,000)
- Haploidentical transplant (half-matched donor): ₹28 lakhs to ₹40 lakhs ($35,000 to $48,000)
- ICU Charges and Hospital Stay: Patients undergoing bone marrow transplant typically require a sterile, high-grade isolation unit, and many spend time in the ICU if complications arise. ICU care and hospital stay combined usually cost between ₹2,00,000 and ₹4,00,000 ($2,400 to $4,800).
- Immunosuppressive Medications and Supportive Drugs: After the transplant, patients need immunosuppressants to prevent graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Antifungal, antiviral, and antibiotic medications are also necessary. Initial medication costs range between ₹1,00,000 and ₹2,50,000 ($1,200 to $3,000).
- Follow-up Consultations and Monitoring: Following discharge, patients undergo routine blood tests, imaging, and clinical reviews to monitor their recovery and progress. The cost of follow-up care in the first three months is usually between ₹50,000 and ₹1,00,000 ($600 to $1,200).
Expense Component | Cost in INR | Cost in USD |
| Pre-Transplant Diagnostics | ₹75,000 – ₹1,50,000 | $900 – $1,800 |
| HLA Typing and Donor Matching | ₹60,000 – ₹1,20,000 | $720 – $1,450 |
| Autologous BMT | ₹12,00,000 – ₹15,00,000 | $14,500 – $18,000 |
| Allogeneic BMT | ₹18,00,000 – ₹25,00,000 | $21,600 – $30,000 |
| ICU & Isolation Ward | ₹2,00,000 – ₹4,00,000 | $2,400 – $4,800 |
| Post-Transplant Medications | ₹1,00,000 – ₹2,50,000 | $1,200 – $3,000 |
| Follow-up Care | ₹50,000 – ₹1,00,000 | $600 – $1,200 |
- Total Estimated Cost of Autologous BMT in India: ₹18,00,000 – ₹25,00,000 ($21,600 – $30,000)
- Total Estimated Cost of Allogeneic BMT in India: ₹25,00,000 – ₹35,00,000 ($30,000 – $42,000)
Cost Comparison: Bone Marrow Transplant in India vs Other Countries
Bone marrow transplant in India offers world-class care at lower costs compared to countries such as the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and Singapore. Overseas patients often choose India because they receive expert treatment at one-third or even one-fifth of the price charged elsewhere, without compromising on quality or safety.
Below is a detailed comparison of BMT costs by type and country.
Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant Cost Comparison:
Country | Cost (in USD) |
| India | $21,600 – $30,000 |
| USA | $100,000 – $150,000 |
| UK | $80,000 – $120,000 |
| Canada | $90,000 – $130,000 |
| Australia | $85,000 – $120,000 |
| Singapore | $60,000 – $90,000 |
| Turkey | $35,000 – $50,000 |
| Thailand | $25,000 – $35,000 |
Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant Cost Comparison:
Country | Cost (in USD) |
| India | $30,000 – $42,000 |
| USA | $200,000 – $350,000 |
| UK | $150,000 – $250,000 |
| Canada | $180,000 – $300,000 |
| Australia | $160,000 – $280,000 |
| Singapore | $100,000 – $180,000 |
| Turkey | $60,000 – $90,000 |
| Thailand | $40,000 – $60,000 |
Why India Is a More Affordable Option
India significantly reduces the financial burden of bone marrow transplant through:
- Lower medical costs without compromising international standards.
- Efficient use of local donor registries reduces delays and expenses in donor matching.
- Inclusive transplant packages that cover diagnostics, isolation wards, ICU charges, medications, and post-discharge care.
- Availability of experienced specialists at top hospitals, such as Fortis Memorial Research Institute, which provides care comparable to that in Western countries.
Patients not only save over 60–80% of the total treatment cost but also benefit from faster scheduling, shorter waiting times, and personalized care.
What Factors Affect Bone Marrow Transplant Cost in India?
While India offers some of the most affordable bone marrow transplant packages globally, several key elements can influence the final treatment cost.
- Type of Bone Marrow Transplant Performed: Autologous transplants (using the patient's own stem cells) are generally less expensive than allogeneic transplants, which require a donor and complex matching procedures. Haploidentical and unrelated donor transplants cost even more due to added testing and logistics.
- Donor Availability and HLA Matching: If a matched sibling donor is available, the cost reduces significantly. However, finding unrelated or haploidentical donors may involve registries, HLA typing, and couriering of stem cells, which adds to the total cost.
- Hospital Infrastructure and Location: Premium hospitals in metropolitan cities, such as Delhi, Mumbai, or Bangalore, often charge more than smaller hospitals. Costs may vary based on room category, ICU setup, and the availability of dedicated BMT units with HEPA filtration.
- Diagnostic and Pre-Transplant Evaluations: Patients undergo extensive testing before transplant, including imaging, cardiac screening, viral markers, and organ function tests. These evaluations can increase the upfront cost.
- Complications and ICU Stay Duration: Some patients may require extended ICU support due to infections, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), or organ failure. Longer stays and intensive care can significantly increase treatment costs.
- Length of Hospitalization and Isolation Care: Bone marrow transplant patients usually remain in protective isolation for 3–4 weeks. If complications arise, the hospitalization period may extend, resulting in increased room, nursing, and supportive care charges.
- Post-Transplant Medications and Supportive Care: Patients often require immunosuppressants, antibiotics, antivirals, and nutritional supplements after discharge from the hospital. The duration and type of medication have a significant impact on the overall cost, especially in allogeneic BMT.
- Follow-up Consultations and Remote Monitoring: Ongoing follow-ups for 3 to 6 months post-discharge are crucial for monitoring recovery and managing complications. These include doctor visits, blood tests, and teleconsultations, which add to the overall budget.
Why Choose India for Bone Marrow Transplant?
India is a global hub for bone marrow transplants due to its blend of advanced medical infrastructure, experienced specialists, and cost-effective care. For international patients seeking high success rates and compassionate treatment without the financial burden, India offers an unmatched combination of quality and affordability.
- World-Class Hospitals with International Accreditation: India is home to globally recognized hospitals, including Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Amrita Hospital, and Max Super Specialty Hospital, which are JCI and NABH accredited. These facilities offer advanced isolation units, HEPA filters, and the latest transplant technologies.
- Expert Hematologists and Transplant Specialists: India boasts some of the world's top BMT doctors, renowned for their expertise in complex cases. These specialists have been trained in the US, UK, and Europe and follow globally accepted protocols.
- Affordable Treatment Packages: Bone marrow transplant in India costs up to 80% less than in Western countries. Hospitals offer transparent, all-inclusive packages that cover everything from diagnosis to post-discharge care.
- Shorter Waiting Times: Unlike the long queues seen in the US or Canada, Indian hospitals are known for faster transplant scheduling. It helps patients receive timely care and increases the chances of recovery.
- Comprehensive Donor Support: India has a growing network of donor registries and advanced HLA-matching labs. These facilities streamline donor identification for allogeneic transplants, reducing delays and costs.
- Seamless Medical Tourism Support: From visa assistance to airport pickup, international help desks at top hospitals ensure a stress-free experience. Multilingual staff and patient coordinators ensure a smooth and culturally sensitive process.
- Excellent Post-Transplant Care and Follow-ups: India offers robust follow-up systems with outpatient support, remote consultations, and easy access to medications. It ensures continuity of care even after patients return home.
What is the Success Rate of Bone Marrow Transplant in India?
India has made significant advancements in hematology and transplant medicine, achieving success rates comparable to top global centers. The outcome depends on factors such as the type of disease, patient age, type of transplant, and the hospital's expertise.
- Autologous Transplant Success Rate: Autologous bone marrow transplants have a higher success rate because there's no risk of graft rejection or GVHD. In India, the success rate typically ranges between 85% and 90%, especially for multiple myeloma and certain types of lymphoma.
- Allogeneic Transplant Success Rate: Allogeneic transplants carry more risks but offer a potential cure for conditions like leukemia, aplastic anemia, and thalassemia. Success rates in India average 65% to 80%, depending on HLA matching, donor type, and the presence of pre-existing infections.
- Matched Sibling Transplant Outcomes: Matched sibling donor transplants exhibit excellent outcomes, with success rates reaching up to 85%, particularly when performed in early disease stages and at specialized centers equipped with isolation facilities.
- Haploidentical and Unrelated Donor Transplants: Due to their increased complexity and higher complication risk, the success rates for haploidentical and unrelated donor transplants range from 50% to 70%. However, Indian hospitals are steadily improving these numbers with the introduction of newer protocols.
Recovery Timeline After Bone Marrow Transplant in India
Recovery from BMT is gradual and varies for each patient. However, most international patients complete the critical phases within a few months under close medical supervision.
- Initial Recovery (First 30 Days): The first month is crucial. Patients remain in isolation to prevent infections while their new marrow begins producing healthy cells. Blood counts are closely monitored, and doctors manage side effects like mucositis or neutropenia.
- Days 30 to 100: Immune Rebuilding Phase: By day 100, most patients exhibit improved blood counts. However, immunity remains weak. Doctors schedule weekly or bi-weekly visits, and patients continue taking immunosuppressants and antifungal/antiviral drugs.
- 3 to 6 Months Post-Transplant: Gradual Strength Gain: Energy levels begin to improve. Most patients return to their basic routines. Children may return to school, and adults can resume non-strenuous work. Regular check-ups ensure early detection of GVHD or infections.
- 6 to 12 Months Post-Transplant: The immune system recovers significantly by the end of the first year. Vaccinations are reintroduced, and long-term medications are tapered. Most patients return to their everyday lives with only minor restrictions.
- Beyond 1 Year: Long-Term Monitoring: Doctors continue to monitor for late complications like chronic GVHD or relapse. Annual reviews, lifestyle adjustments, and periodic bone marrow biopsies are essential for ensuring long-term success and stability.
Bone Marrow Transplant - BMT Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Bone Marrow Transplant - BMT costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $21,600 - $42,000 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
Leading Hospitals for Bone Marrow Transplant - BMT in India

SP Medifort Hospital
SP Medifort, Thiruvananthapuram, is a JCI-accredited, 475-bed multi-super-specialty hospital spread across 500,000 sq. ft. The hospital houses 10 modu...
Accreditations


Facilities

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, is a 435-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital with 120 critical care beds. Established in 20...
Accreditations

Facilities

AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, is a 1,000-bed, JCI- and NABH-accredited super-specialty hospital spanning 1.7 million sq. ft. It is the flagshi...
Accreditations


Facilities

Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai
Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai, is a 200-bed quaternary-care hospital and part of the IHH Healthcare network, one of the world’s largest priva...
Accreditations

Facilities

MGM Healthcare, Chennai
MGM Healthcare, Chennai, is a 400-bed quaternary-care super-specialty hospital accredited by JCI, NABH, and NABL. The hospital features 100 ICU beds,...
Accreditations


Facilities

MIOT International, Chennai
MIOT International, Chennai, is a 1,000-bed NABH- and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital serving patients from more than 130 countries. Establish...
Accreditations

Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai, is the flagship hospital of the Apollo Group. Established in 1983, it has 560 beds, 46 ICUs, and 15 operating...
Accreditations



Facilities

HCG Cancer Centre, Mumbai
HCG Cancer Centre, Borivali, Mumbai, is an NABH- and AACI-accredited comprehensive cancer hospital established in 2019. The 119-bedded facility includ...
Accreditations


Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, established in 2016, is a 500-bed JCI- and NABH-accredited quaternary care hospital offering advanced treatment across...
Accreditations


Facilities

Marengo Asia Hospitals, Faridabad
Marengo Asia Hospital, formerly QRG Health City, is a 325-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital in Faridabad. It offers advanced care i...
Accreditations

Facilities
Gallery

FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Related Procedures
Other procedures in this department
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
