Kidney Transplant Cost in India
About Kidney Transplant
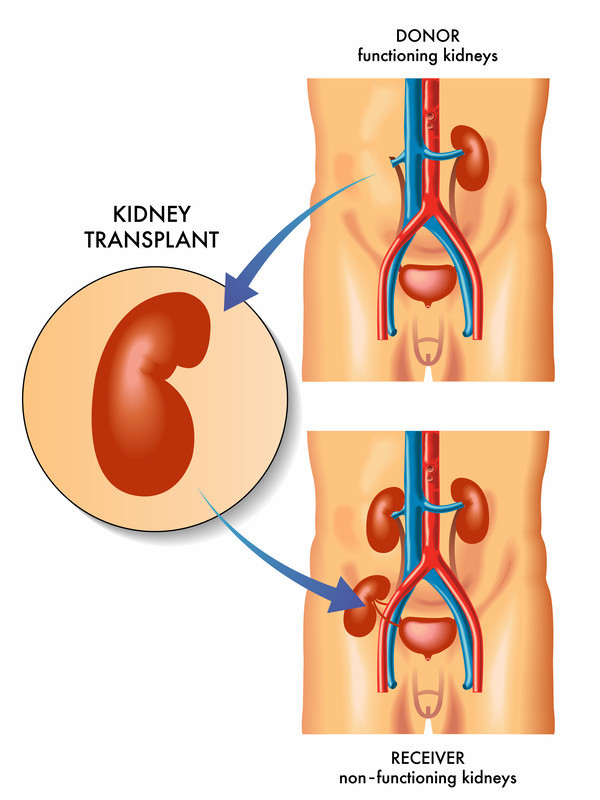
What Is a Kidney Transplant?
A kidney transplant is a life-saving surgical procedure used to treat patients with end-stage kidney failure or chronic kidney disease when their kidneys cannot filter waste and fluids from the blood effectively. Instead of relying on long-term dialysis, the patient receives a healthy kidney from a donor, which is then surgically implanted into their body to take over the functions of the diseased kidney.
The donor kidney can come from a living donor (a family member or close relative) or a deceased donor (an individual who has consented to organ donation after death). Only one functioning kidney is generally sufficient for a healthy life, making kidney donation a viable option without harming the donor's long-term health.
When Is a Kidney Transplant Needed?
A kidney transplant is typically recommended when both kidneys have lost more than 85% to 90% of their function, and the person has entered end-stage renal disease (ESRD) — the final stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD). At this point, the kidneys are no longer able to effectively filter blood, remove waste, or regulate fluid and electrolyte balance, resulting in the accumulation of toxins in the body.
Most patients at this stage are initially put on dialysis, which acts as an artificial kidney. However, dialysis is time-consuming, often requires several visits per week to a hospital or clinic, and over time, can take a toll on a patient's health and quality of life.
A kidney transplant becomes necessary in the following situations:
- The patient is experiencing frequent complications from dialysis, such as infections, blood pressure instability, or vascular access failure.
- Blood tests show progressive deterioration in kidney function (usually GFR <15 ml/min).
- There are signs of fluid overload, anemia, bone disease, or other symptoms linked to poor kidney function that are not controlled by dialysis or medication.
- The patient wants to avoid a lifetime of dialysis and is deemed physically and emotionally ready for a transplant.
In some cases, preemptive transplantation is considered, where a patient undergoes a transplant before starting dialysis, provided a suitable donor is available. This option often yields better outcomes, including prolonged graft survival and improved quality of life.
Common diseases that may lead to kidney failure include:
- Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes (diabetic nephropathy)
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Polycystic kidney disease (a genetic condition)
- Chronic glomerulonephritis
- Recurrent kidney infections or obstructions
Why a Transplant Is Better Than Long-Term Dialysis
While dialysis can keep a patient alive by removing waste products from the blood, it comes with significant lifestyle limitations and long-term health risks. A successful kidney transplant:
- Improves life expectancy
- Enhances quality of life
- Offers freedom from regular dialysis sessions
- Allows patients to return to work or normal daily activities
Many patients who receive a kidney transplant enjoy a near-normal lifestyle with a functioning new kidney that can last 10–20 years or more, especially with proper medical care and follow-up.
Who Is Eligible for a Kidney Transplant?
Not all patients with kidney failure are eligible for a transplant. Eligibility for kidney transplantation depends on a range of medical, psychological, and logistical factors. The goal is to ensure that both the recipient and donor (if living) are healthy enough for surgery and that the transplant has the best chance of long-term success.
Key Criteria for Recipient Eligibility:
- Confirmed Diagnosis of ESRD: The patient must have end-stage renal disease (ESRD), typically defined as a glomerular filtration rate of less than 15 mL/min.
- Age and Physical Fitness: While there is no fixed age limit, most transplant centers prefer patients under 70 who are otherwise in good physical health. Older patients may still be eligible if they are physically fit and have no significant risk factors.
- Absence of Uncontrolled Infections or Active Cancer: Patients should be free from tuberculosis, hepatitis, or cancer. If previously treated for cancer, a disease-free period may be required.
- Heart and Lung Health: A strong cardiovascular system is crucial since the surgery involves anesthesia and can stress the heart and lungs.
- Commitment to Post-Transplant Care: Patients must be mentally sound and committed to taking daily immunosuppressive medications, and they must attend regular follow-up visits.
- No Substance Abuse: Active use of alcohol, drugs, or tobacco may delay or disqualify a transplant due to the risks they pose to post-operative care
For Living Donor Transplants:
- The donor must be between 18 and 65 years old, mentally competent, and willing to donate voluntarily.
- Donors must undergo thorough evaluations to ensure they have two healthy kidneys and no medical conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or kidney disease themselves.
- In India, living donors must be a close relative (parents, siblings, spouse, or children) as per the Transplantation of Human Organs Act (THOA). Non-related donors require special ethical and legal clearances.
What are the Different Types of Kidney Transplant Procedures?
Kidney transplantation isn't a one-size-fits-all surgery. The type of transplant procedure depends primarily on the source of the donor kidney, the urgency of the transplant, and the recipient's medical condition.
Living Donor Kidney Transplant
It is the most common and preferred type of transplant, especially in countries like India. In this procedure, a healthy person (usually a family member) donates one of their kidneys to the patient. Since only one healthy kidney is needed for survival, living donation is both safe and highly effective.
There are two subtypes:
- Related Living Donor Transplant: The donor is a close blood relative, such as a parent or child. It usually results in better compatibility and fewer chances of rejection.
- Unrelated Living Donor Transplant: The donor is not biologically related but may be emotionally connected (e.g., a spouse or friend). Legal and ethical approvals are mandatory in such cases under Indian law.
Advantages:
- Shorter waiting time
- Better organ match
- Higher long-term success rate
Deceased Donor (Cadaveric) Kidney Transplant
In a deceased donor kidney transplant, the kidney is retrieved from a brain-dead donor who had previously consented to organ donation or whose family approved the donation. Deceased donor transplants are less common in India due to lower organ donation rates, but awareness is improving.
The recipient is usually placed on a waiting list, and the transplant is performed when a compatible organ becomes available.
Advantages:
- Suitable for patients who don't have a living donor
- Expands access to transplantation for more people
Disadvantages:
- Longer waiting periods
- Slightly lower survival rates compared to living donor kidneys
ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplant
Traditionally, kidney transplants required the donor and recipient to have matching blood groups. However, with advancements in immunosuppressive therapy and plasmapheresis (a process that removes antibodies from the blood), it is now possible to perform successful ABO-incompatible transplants.
It is beneficial when a willing living donor is not blood group compatible. The patient undergoes special treatment before the transplant to reduce the risk of rejection.
Considerations:
- Slightly higher cost due to additional pre-transplant treatment
- Increased risk of complications, though success rates have improved significantly
Preemptive Kidney Transplant
It is a proactive transplant performed before the patient begins dialysis. It is ideal for individuals with progressive chronic kidney disease and a willing donor. Research shows that preemptive transplants lead to:
- Better long-term kidney function
- Lower complication rates
- Improved quality of life
Not all patients qualify, but for those who do, it's considered the gold standard of care.
Send Query
About Kidney Transplant in India
How Is a Kidney Transplant Done in India?
India has become a global destination for kidney transplant surgery, thanks to its advanced medical infrastructure, skilled transplant teams, and personalized care. Below is a clear step-by-step overview of how a kidney transplant is typically performed in Indian hospitals.
Step 1: Pre-Transplant Evaluation
Before undergoing a transplant, both the recipient and donor (if living) undergo comprehensive medical evaluations. These include:
- Blood tests (ABO and HLA typing)
- Imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scan, chest X-ray)
- Cardiac and respiratory assessments
- Psychological and counseling sessions
It ensures both are medically fit and that the recipient's immune system will accept the donor organ.
Step 2: Donor Matching and Legal Clearance
If a living donor is involved, blood group and tissue compatibility are checked. For unrelated donors, special approvals are required through an Authorization Committee under Indian transplant laws.
For deceased donor transplants, the patient must register with a government-regulated waiting list, and matching is done based on urgency and compatibility.
Step 3: Admission and Pre-Surgery Preparation
Once the transplant is cleared, both donor and recipient are admitted to the hospital 1–2 days prior. Medical staff prepare the recipient's body by adjusting medications and conducting final checks. Consent forms are reviewed, and immunosuppressive therapy may be initiated before surgery.
Step 4: Transplant Surgery
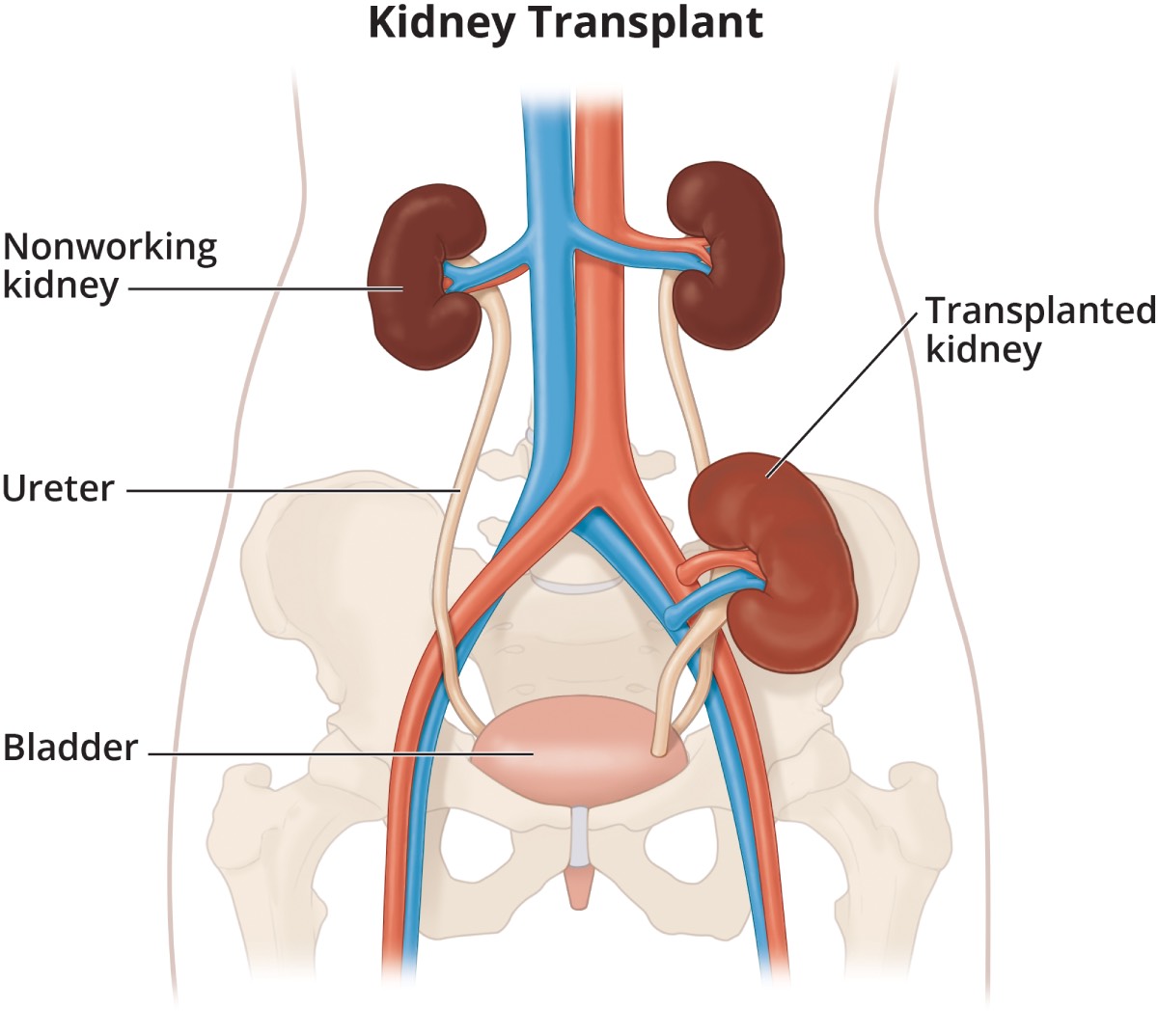
The surgery is a little bit long and takes 3 to 4 hours. It is typically performed under general anesthesia. The donated kidney is placed in the lower abdomen (not the original kidney location), and the blood vessels and ureter are connected to allow proper blood flow and urine output.
- In living donor transplants, the donor kidney is removed laparoscopically or via a small incision.
- The old kidneys are usually not removed unless there is chronic infection or complications.
Step 5: Post-Operative Recovery
After surgery, the recipient is moved to a high-dependency unit or ICU for monitoring. Most KT patients stay in the hospital for 7 to 10 days. The donor is discharged in 3 to 5 days, depending on their recovery.
Immunosuppressive medications begin immediately to prevent organ rejection. Patients receive:
- Infection control treatment
- Pain management
- Nutritional guidance
- Fluid and electrolyte monitoring
Use of Advanced Immunosuppressants and Techniques in India
Indian transplant hospitals use the latest-generation immunosuppressants such as tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil, and biologics (like basiliximab or thymoglobulin) that reduce rejection risks without weakening the immune system too much.
Additionally, many Indian centers adopt:
- Minimally invasive laparoscopic donor nephrectomy to reduce donor recovery time
- Plasmapheresis and desensitization for ABO-incompatible transplants
- Real-time ultrasound and Doppler guidance for accurate vascular anastomosis
- Electronic medication monitoring systems for post-transplant adherence
What is the Cost of a Kidney Transplant in India?
The cost of a kidney transplant in India is more affordable compared to many Western and Middle Eastern countries, making it a preferred destination for overseas patients. On average, the cost of a kidney transplant in India ranges from ₹6,00,000 to ₹10,00,000, which is approximately $7,000 to $12,000.
Kidney Transplant Cost Breakdown in India
Component | Estimated Cost (INR) | Estimated Cost (USD) | Description |
| Initial Consultation and Evaluation | ₹50,000 – ₹1,00,000 | $600 – $1,200 | Includes nephrologist and transplant surgeon consultation, blood tests, and imaging. |
| Donor Compatibility and Testing | ₹70,000 – ₹1,20,000 | $850 – $1,400 | Covers HLA typing, cross-matching, and full donor workup. |
| Surgical Procedure | ₹2,00,000 – ₹3,50,000 | $2,400 – $4,200 | Includes surgery fees, anesthesia, OT charges, and donor operation if applicable. |
| Hospital Stay (10–14 days) | ₹1,00,000 – ₹2,00,000 | $1,200 – $2,400 | Covers standard ward or private room, ICU if required, and nursing care. |
| Post-Operative Medications | ₹50,000 – ₹1,50,000 | $600 – $1,800 | Includes immunosuppressants and infection-prevention drugs. |
| Follow-Up Visits and Monitoring | ₹30,000 – ₹80,000 | $350 – $950 | Includes regular check-ups, bloodwork, and drug-level monitoring. |
| Miscellaneous and Admin Costs | ₹20,000 – ₹50,000 | $240 – $600 | Legal documentation, diet planning, physiotherapy, and local logistics. |
It is an all-inclusive estimate for both the recipient and donor, making India one of the most affordable and transparent destinations for kidney transplant surgery worldwide.
What's Included in the Cost of a Kidney Transplant in India?
Most hospitals offer comprehensive transplant packages that typically include:
- Donor and recipient evaluation: Blood group matching, HLA typing, cross-matching, cardiac and kidney function tests, and imaging
- Legal documentation and authorization processing: Especially for unrelated or foreign donors
- Surgical procedures: Kidney harvesting (for living donors), transplant surgery, anesthesia, and surgical team charges
- Hospital stay: 7–10 days for the recipient and 3–5 days for the donor, including ICU and ward charges
- Post-surgery medications: Including immunosuppressants during the initial hospital stay
- Follow-up consultations: Post-discharge recovery supervision and lab monitoring during the first few weeks
Please note: Additional expenses may apply if there are complications, need for plasmapheresis, or long-term follow-up beyond the included stay.
Kidney Transplant Cost Comparison: India vs Other Countries
India provides world-class kidney transplant services at the most affordable rates globally. For patients from Africa, the Middle East, South Asia, and even developed nations, choosing India means accessing quality care, expert surgeons, and comprehensive treatment packages, all at one-fifth or less of the cost in other countries.
Country | Kidney Transplant Cost (Approx.) |
| India | $7,000 – $12,000 (₹6 – ₹10 lakh) |
| USA | $300,000 – $400,000 |
| UK | $70,000 – $100,000 |
| UAE | $40,000 – $70,000 |
| Thailand | $18,000 – $25,000 |
Why Is Kidney Transplant in India So Affordable?
There are several reasons why India can offer kidney transplant procedures at a fraction of the cost charged in countries like the USA, UK, or UAE, without compromising the standard of care:
- Lower operating and infrastructure costs in Indian hospitals
- Highly skilled surgeons are available at much lower fees than their Western counterparts
- Economic cost of medications, including immunosuppressants, produced locally
- Government-regulated healthcare pricing in many states and private hospitals
Kidney Transplant Costs Based on Patient Condition
The actual cost of a kidney transplant in India can vary based on several real-life clinical situations. These variations depend on the complexity of the case, the donor type, the need for desensitization, and the post-operative recovery duration. Below are some practical cost scenarios to help international patients understand what to expect.
- Standard Kidney Transplant with Living Related Donor: For patients undergoing a planned kidney transplant with a healthy, HLA-matched living donor (such as a sibling or parent), the total cost typically ranges from ₹6,00,000 to ₹7,00,000 (approximately $7,000 to $8,500). It includes evaluation, surgery, hospital stay, and essential medications.
- ABO-Incompatible Kidney Transplant: If the donor has an incompatible blood group, special procedures like plasmapheresis and immunoadsorption are required before transplant. It increases the overall cost from ₹8,00,000 to ₹10,00,000 (around $9,500 to $12,000). These transplants are becoming increasingly common in India due to advancements in immunosuppressive protocols.
- Kidney Transplant from a Deceased Donor: In case of a deceased donor (cadaveric transplant), additional registration, waiting period, and ICU monitoring may be needed. The cost usually falls within ₹6,50,000 to ₹8,50,000 ($7,500 to $10,000), depending on how long the recipient needs pre-transplant hospitalization.
- Pediatric Kidney Transplant: For children needing kidney transplantation, the cost can rise slightly due to the need for pediatric ICU care, specialized surgeons, and tailored drug regimens. On average, the price ranges from ₹7,00,000 to ₹9,00,000 (roughly $8,000 to $11,000).
- Complex Cases with Comorbidities: Patients with pre-existing conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or cardiac issues may need extra diagnostics and longer recovery time. In such cases, the total transplant cost may range from ₹10,00,000 to slightly higher ($12,000 or more), depending on the complexity.
What are the Factors Affecting Kidney Transplant Cost in India?
While India offers some of the most affordable kidney transplant packages in the world, the final cost can still vary from patient to patient. Several medical and logistical factors come into play, such as donor compatibility, hospital selection, recovery duration, and post-transplant care.
- Type of Donor (Living or Deceased): Transplants from living, related donors are generally more affordable and can be planned. Deceased donor transplants may require longer ICU stays and emergency logistics, raising overall costs.
- Donor-Recipient Compatibility: If the donor has an incompatible blood group or tissue mismatch, additional treatments like plasmapheresis or desensitization are needed. These procedures significantly increase the cost of the transplant.
- Hospital and City of Treatment: Top-tier transplant hospitals in metro cities like Hyderabad or Bangalore may charge more due to advanced infrastructure and higher service standards. However, they also offer better surgical outcomes and post-op care.
- Room Type and Length of Hospital Stay: Choosing a private deluxe room over a shared ward results in higher accommodation charges. Additionally, any complications that necessitate an extended stay in the ICU or inpatient care will be factored into the final bill.
- Medication and Immunosuppressant Costs: Initial post-transplant drugs are potent and expensive. The cost of lifelong immunosuppressive medication, particularly during the first 6–12 months, significantly contributes to the total expenditure.
- Patient's Overall Health and Comorbidities: Patients with diabetes, hypertension, or heart conditions may require additional tests, consultations, and a longer recovery time. These add to the diagnostic and monitoring costs.
- Legal and Regulatory Documentation: Foreign patients often require additional documentation and legal clearances for ethical donor evaluation and transplant approval, which can increase administrative expenses.
- Post-Transplant Monitoring and Complication Management: Unexpected complications, such as rejection or infection, may require ICU care, dialysis, or re-admission. It results in higher out-of-pocket costs beyond the standard package.
International Patient Services for Kidney Transplant in India
India is renowned not only for its affordable treatment but also for offering world-class support services specifically designed for international patients. These value-added services ensure that your kidney transplant journey is safe, smooth, and stress-free.
- Dedicated International Patient Coordinators: Most top hospitals in India have specialized teams that handle everything from visa letters to airport pickups. These coordinators act as your point of contact throughout the treatment process.
- Assistance with Medical Visa and Travel Arrangements: Hospitals often help in issuing medical invitation letters, scheduling embassy appointments, and guiding patients through the medical visa process. They also assist with booking affordable flights and local transfers.
- Language Translation Support: Professional interpreters are available in many Indian hospitals to assist patients from Arabic, French, Russian, Swahili, Bengali, and Spanish-speaking countries.
- Affordable Accommodation for Family Members: Hospitals often provide on-campus or nearby guest houses and partner hotels at discounted rates, making it easier for family members or attendants to stay comfortably during the recovery period.
- Pre-Arrival Medical Opinion: You can share your reports before traveling and receive a free treatment plan and cost estimate from a senior nephrologist.
- Post-Treatment Follow-up via Telemedicine: After discharge, many Indian hospitals offer online video consultations, prescription support, and ongoing monitoring through telehealth platforms.
Concierge Services for Local Support: Some hospitals provide services such as currency exchange, SIM card arrangement, medical interpreters, and city tours for family members, making the experience more patient-friendly.
Kidney Transplant Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Kidney Transplant costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $7,000 - $12,000 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
Leading Hospitals for Kidney Transplant in India

SP Medifort Hospital
SP Medifort, Thiruvananthapuram, is a JCI-accredited, 475-bed multi-super-specialty hospital spread across 500,000 sq. ft. The hospital houses 10 modu...
Accreditations


Facilities

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, is a 435-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital with 120 critical care beds. Established in 20...
Accreditations

Facilities

AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, is a 1,000-bed, JCI- and NABH-accredited super-specialty hospital spanning 1.7 million sq. ft. It is the flagshi...
Accreditations


Facilities

Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai
Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai, is a 200-bed quaternary-care hospital and part of the IHH Healthcare network, one of the world’s largest priva...
Accreditations

Facilities

MGM Healthcare, Chennai
MGM Healthcare, Chennai, is a 400-bed quaternary-care super-specialty hospital accredited by JCI, NABH, and NABL. The hospital features 100 ICU beds,...
Accreditations


Facilities

MIOT International, Chennai
MIOT International, Chennai, is a 1,000-bed NABH- and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital serving patients from more than 130 countries. Establish...
Accreditations

Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai, is the flagship hospital of the Apollo Group. Established in 1983, it has 560 beds, 46 ICUs, and 15 operating...
Accreditations



Facilities

HCG Cancer Centre, Mumbai
HCG Cancer Centre, Borivali, Mumbai, is an NABH- and AACI-accredited comprehensive cancer hospital established in 2019. The 119-bedded facility includ...
Accreditations


Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, established in 2016, is a 500-bed JCI- and NABH-accredited quaternary care hospital offering advanced treatment across...
Accreditations


Facilities

Marengo Asia Hospitals, Faridabad
Marengo Asia Hospital, formerly QRG Health City, is a 325-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital in Faridabad. It offers advanced care i...
Accreditations

Facilities
Gallery

FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Related Procedures
Other procedures in this department
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
