Liver Transplant Cost in India
About Liver Transplant
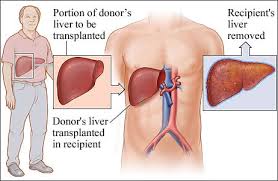
What Is a Liver Transplant?
A liver transplant is a life-saving surgical procedure where a diseased/damaged liver is replaced with a healthy liver from another person. This new liver can come from either a living donor (who gives a portion of their liver) or a deceased donor (who donates their liver after death). The liver is an important body organ that plays a crucial role in digestion, removing toxins from the blood, and storing essential nutrients. Without a working liver, the body starts to shut down.
In many serious liver diseases, medication and other treatments may no longer help. At this point, a liver transplant becomes the only chance for survival. The surgery removes the damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy one that can perform all essential functions.
Who Needs a Liver Transplant?
Not everyone with liver disease needs a transplant. But when the liver begins to fail and can no longer keep the body healthy, doctors start considering a liver transplant. This life-saving surgery is often the best option for end-stage liver disease patients or those having certain types of liver cancer.
Common Conditions That Require a Liver Transplant
Liver failure often develops gradually in many people, typically after months or years of accumulated damage has occurred. The most common reasons someone might need a transplant are:
- Cirrhosis: This is the most frequent cause. In cirrhosis, the liver tissue becomes scarred and hardened, which stops blood flow and impairs healthy liver function. Alcohol abuse, hepatitis, and fatty liver disease often lead to cirrhosis.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This happens when fat accumulates in the liver, causing inflammation over time.
- Long-term Hepatitis B or C: Chronic viral infections damage liver cells and gradually lead to liver failure.
- Liver Cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma): In some cases, cancer that starts in the liver can still be cured if detected early and a transplant is performed.
- Acute Liver Failure: This is a sudden loss of liver function, often due to drug overdose (like paracetamol), infections, or toxic exposure.
How Do Doctors Decide Eligibility?
Doctors don't suggest a transplant right away. First, they run several tests to check how well the liver is working. The MELD score (Model for End-Stage Liver Disease) helps doctors decide when a transplant is needed. The higher the score, the greater the urgency.
Patients also need to meet other conditions. For example, they must:
- Be healthy enough to undergo major surgery.
- Have no active infections or cancer outside the liver.
- Show signs they will follow post-transplant care instructions.
Doctors also evaluate emotional and mental readiness. Since liver transplant recovery requires lifelong care and medicine, patients must show a strong commitment to staying healthy.
What are the Different Types of Liver Transplants?
Liver transplant surgery is available in various forms, depending on the patient's medical condition, donor availability, and the urgency of the procedure. Each type of liver transplant has its own set of advantages and is selected after a thorough medical evaluation by the transplant team.
Living Donor Liver Transplant
A living donor liver transplant procedure involves taking a portion of the liver (usually the right or left lobe) from a healthy living person and transplanting it into the recipient. This type of transplant is possible because the liver has a unique ability to regenerate to its full size in both the donor and the recipient within a few weeks after surgery.
Living donor liver transplants are best suited for children or adults who have a willing and medically fit family member or friend as a donor. The main advantages of this type include shorter waiting times, the ability to schedule the surgery in advance, and a higher success rate due to better organ quality and timing.
Deceased Donor Liver Transplant
A deceased donor liver transplant uses a full liver from a person who has recently died and has donated their organs. The liver is carefully preserved and transplanted into the patient within a critical time window after removal.
A deceased donor liver transplant is recommended for patients who do not have an eligible living donor. However, it may involve longer waiting times due to the limited availability of suitable deceased donor organs. It is commonly performed in patients with end-stage liver disease or acute liver failure.
Split Liver Transplant
Split liver transplant surgery involves dividing a deceased donor's liver into two parts, which are then transplanted into two different recipients, typically one adult and one child. It is a highly specialized procedure and requires excellent surgical precision and hospital infrastructure.
Split liver transplants are beneficial because they allow two lives to be saved with a single donated liver. The technique is often used in pediatric liver transplant cases where the recipient requires a smaller graft.
Auxiliary Liver Transplant
An auxiliary liver transplant involves implanting a partial donor liver alongside the patient's own diseased liver, instead of replacing it entirely. This method is considered when there is a possibility that the native liver may recover over time, such as in cases of acute liver failure due to poisoning or viral hepatitis.
Auxiliary liver transplantation is mainly used in younger patients or in situations where the doctors want to preserve the original liver function. If the patient's liver recovers, the donor graft may shrink or even be removed in a later procedure.
How is a Liver Transplant Performed?
The liver transplant process follows a carefully structured protocol to ensure the best outcomes. The entire journey includes evaluation, donor selection, surgical procedure, and postoperative recovery. Understanding each step helps patients and their families prepare mentally, physically, and financially.
Pre-Transplant Evaluation
Surgeons begin the process by conducting a thorough medical assessment to confirm that liver transplant surgery is the best treatment option. The evaluation includes blood tests, imaging scans, assessments of heart and lung function, and psychological counseling.
The transplant team also checks for any contraindications, like uncontrolled infections or severe heart disease. Only those who meet the eligibility criteria move forward in the transplant process.
Donor Matching and Preparation
If the patient has a living donor, doctors perform compatibility tests to ensure a safe match. For a deceased donor transplant, the patient's name is added to the transplant waiting list. Matching involves checking blood type, liver size, and general health.
Once a suitable donor is confirmed, both donor and recipient undergo final medical checks and pre-surgical planning. In the case of a living donor, the transplant date is scheduled in advance.
Liver Transplant Surgery
The surgery takes place in a sterile operating room equipped with advanced liver transplant technology. Transplant surgeons remove the diseased liver and replace it with a healthy liver or liver segment from the donor.
The operation usually lasts 8 to 12 hours. Experienced liver transplant surgeons work alongside anesthesiologists and support staff to minimize risks and ensure precision.
Immediate Post-Surgery ICU Care
After surgery, the patient is shifted to the intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring. Doctors regularly check vital signs, liver function, and the body's response to the new organ.
During the ICU stay, patients receive immunosuppressant medications to prevent organ rejection and antibiotics to ward off infections.
Hospital Stay and Recovery
The hospital stay after a liver transplant in India ranges from 2 to 3 weeks. Patients gradually begin walking, eating, and resuming basic activities under medical supervision.
The transplant team educates the patient and caregivers on hygiene, nutrition, wound care, and medication schedules prior to discharge.
Long-Term Follow-Up and Monitoring
After discharge, patients attend regular follow-up visits for the first few months. These visits include blood tests, ultrasound scans, and adjustments in medication doses.
Doctors monitor for signs of organ rejection, infections, and other complications. Long-term care helps ensure the liver functions well and the patient remains healthy.
Send Query
About Liver Transplant in India
What is the Cost of a Liver Transplant in India?
The liver transplant cost in India ranges between ₹20 lakhs to ₹30 lakhs, which is approximately $23,000 to $36,000. It includes most of the essential services required for a successful transplant and postoperative recovery. Compared to countries like the United States or the United Kingdom, India offers world-class liver transplant services at a significantly lower price.
What's Included in the Liver Transplant Package in India?
Most liver transplant packages in India cover a comprehensive list of medical and surgical services, which include:
- Pre-transplant evaluation: This includes blood tests, imaging scans (such as MRI or CT), liver function tests, and cardiopulmonary assessments. These tests help determine whether the patient is fit for transplant.
- Surgical procedure charges: The actual cost of liver transplant surgery includes operating theater charges, surgeon's fees, anesthetist fees, and the cost of medical equipment used during the procedure.
- Donor surgery expenses: In the case of a living donor liver transplant, the cost also includes evaluation, hospitalization, and surgery for the donor.
- Intensive Care Unit (ICU) stay: The transplant recipient requires ICU support for several days post-surgery to monitor vital signs and manage complications.
- Hospital stay for both donor and recipient: Typically, recipients remain in the hospital for 2 to 3 weeks while donors stay for about a week.
- Immunosuppressive medications: These are critical drugs that prevent the immune system from rejecting the transplanted liver. The initial cost of these medications is included in the package.
- Nursing and ward care: High-quality postoperative care is provided by trained nurses and medical staff to ensure proper recovery.
- Follow-up consultations (initial period): Some hospitals include a few months of follow-up visits, blood tests, and follow-up monitoring in the overall transplant cost.
India's liver transplant centers also offer value-added services, such as dietary planning, physiotherapy, and counseling, particularly for international patients, as part of a comprehensive care plan.
Cost Breakdown of Liver Transplant in India
The complete cost structure of liver transplant in India includes various stages such as medical evaluations, surgery, hospital stay, medications, and donor care. Below is a detailed cost breakdown of what you can expect.
- Pre-Transplant Evaluation Cost: Doctors perform several diagnostic tests before scheduling the surgery. These include blood tests, imaging scans, cardiac evaluations, and consultations with specialists. The cost for liver transplant pre-evaluation ranges between ₹1,50,000 and ₹2,50,000 (approximately $1,800 to $3,000).
- Liver Transplant Surgery Cost: The surgical cost of liver transplant covers the operation theater, surgeon's fee, anesthetist, surgical team, and equipment. It is the most considerable portion of the expense, ranging from ₹10 lakhs to ₹15 lakhs ($12,000 to $18,000).
- Donor Surgery and Care Cost: In living donor transplants, the donor also undergoes surgery. It includes hospital admission, donor evaluation, and surgical fees. The donor surgery cost in India ranges from ₹3 lakhs to ₹5 lakhs ($3,500 to $6,000).
- Postoperative ICU and Hospital Stay: Patients typically spend several days in the ICU, followed by recovery in a general ward or private room. The ICU and hospitalization cost ranges between ₹3 lakhs and ₹4 lakhs ($3,500 to $4,800).
- Immunosuppressive Medication Cost: After transplant, patients need lifelong medications to prevent organ rejection. The initial cost of the immunosuppressive drug is approximately ₹1 lakh to ₹1.5 lakh ($1,200 to $1,800), which may increase depending on the patient's response to treatment.
- Follow-up Tests and Consultation Charges: After discharge, doctors continue to monitor the patient's progress through regular blood tests and check-ups. The first few months of follow-up care can cost between ₹50,000 and ₹1,00,000 ($600 to $1,200).
Expense Component | Cost in INR | Cost in USD |
| Pre-transplant Evaluation | ₹1,50,000 – ₹2,50,000 | $1,800 – $3,000 |
| Liver Transplant Surgery | ₹10,00,000 – ₹15,00,000 | $12,000 – $18,000 |
| Donor Surgery and Care | ₹3,00,000 – ₹5,00,000 | $3,500 – $6,000 |
| ICU & Hospital Stay | ₹3,00,000 – ₹4,00,000 | $3,500 – $4,800 |
| Immunosuppressive Medications | ₹1,00,000 – ₹1,50,000 | $1,200 – $1,800 |
| Follow-up Care | ₹50,000 – ₹1,00,000 | $600 – $1,200 |
| Total Estimated Cost | ₹20,00,000 – ₹30,00,000 | $23,000 – $36,000 |
Liver Transplant Cost Comparison: India vs Other Countries
India is a preferred destination for liver transplant surgery because of its cost-effectiveness without compromising on quality. When comparing liver transplant costs globally, India consistently offers some of the most affordable options while maintaining excellent outcomes.
In countries such as the United States or the United Kingdom, the total cost of a liver transplant can be overwhelming. Patients often face long waiting times and high out-of-pocket expenses due to insurance deductibles. On the other hand, Indian hospitals provide world-class liver transplant procedures at a fraction of the international cost.
Country | Average Liver Transplant Cost (USD) | Key Highlights |
| India | $23,000 – $36,000 | Affordable, shorter wait time, skilled surgeons |
| United States | $5,00,000 – $8,00,000 | Very high cost, long waiting period |
| United Kingdom | $3,00,000 – $4,50,000 | High cost, availability mostly through the NHS |
| UAE | $1,20,000 – $2,00,000 | Expensive, limited number of transplant centers |
| Turkey | $70,000 – $1,00,000 | Growing medical hub, still costlier than India |
| Singapore | $2,50,000 – $3,50,000 | High-tech facilities but high cost |
India stands out as a country that provides advanced liver transplant surgeries at economical rates. Even after including travel, accommodation, and postoperative recovery costs, the total expense in India remains significantly lower than in most developed nations.
Additionally, Indian hospitals provide comprehensive support to international patients, ensuring a smooth and stress-free process. Choosing India for a liver transplant not only saves money but also reduces waiting time, improves access to skilled doctors, and ensures personalized care.
What are the Factors Affecting Liver Transplant Cost in India?
The liver transplant cost in India can vary widely based on several critical elements related to both the patient and the healthcare facility. These factors influence overall medical expenses, and understanding them provides patients with better clarity on what to expect financially.
- Type of Liver Transplant: Living donor liver transplant usually costs more because it includes two surgeries, one for the donor and one for the patient. Deceased donor transplant may involve costs for coordination and organ matching.
- Hospital and City: The cost of a liver transplant varies depending on the hospital's reputation and location. Premium hospitals in metro cities like Delhi or Mumbai may charge more due to advanced facilities and expert teams.
- Surgeon's Experience: Surgeons with years of transplant experience may charge higher fees. However, their skills often lead to better outcomes and fewer complications.
- Patient's Health Condition: If the patient has advanced liver failure or multiple health issues, they may require additional tests, a more extended ICU stay, and more medications, which can increase the overall cost.
- Donor-Related Expenses: A living donor transplant includes donor screening, surgery, and postoperative care. These services are billed along with the recipient's transplant package.
- Length of Hospital Stay: Patients who recover slowly or need ICU care for longer periods will incur higher hospital bills. The length of hospital stay directly impacts total expenses.
- Post-Transplant Medicines: Immunosuppressants and follow-up tests are essential after surgery. These long-term medications can increase the overall cost by several lakhs.
Why Choose India for Liver Transplant?
India has become one of the top destinations for liver transplants due to its blend of affordability and high medical standards. Patients from across the globe travel here to receive expert care without compromising on quality.
- World-Class Surgeons with Global Training: India boasts some of the most experienced liver transplant surgeons, who have received training at leading institutions worldwide. Their expertise ensures safe procedures and excellent outcomes.
- Advanced Hospitals with Modern Infrastructure: Top hospitals in India offer cutting-edge technology, advanced ICUs, and dedicated transplant units. These facilities follow strict international protocols for safety, hygiene, and postoperative care.
- Affordable Liver Transplant Packages: Liver transplants in India are significantly less expensive than those in countries like the US or the UK. Despite the lower cost, patients receive comprehensive care, including donor surgery and intensive aftercare.
- High Donor Availability and Efficient Coordination: India has a growing living donor program and is steadily improving deceased donor networks. Hospitals here are adept at managing the complex logistics of transplant coordination.
- Minimal Waiting Time and Faster Procedures: Compared to the long waiting lists in many Western countries, India offers quicker evaluation, faster matching, and prompt surgery scheduling, which is critical for patients with urgent liver conditions.
- Holistic Care for International Patients: From visa assistance and travel planning to local language support and post-discharge guidance, Indian hospitals offer a smooth experience for foreign patients seeking liver transplant treatment.
What Services are Provided to Overseas Patients?
India offers a comprehensive range of support services to ensure that overseas patients feel safe, comfortable, and well cared for throughout their liver transplant journey. These services make the entire process, from planning to recovery, stress-free and efficient.
- Dedicated Case Managers for Personalized Care: Each patient is assigned a case manager who acts as the single point of contact. The manager helps coordinate appointments, doctor consultations, surgery schedules, and follow-ups, ensuring seamless communication throughout the treatment.
- Visa Assistance and Medical Invitations: Hospitals in India provide official visa invitation letters (VILs) and help patients and their caregivers with visa applications. Many institutions have tie-ups with embassies to expedite the process.
- Airport Pick-up and Local Travel Support: Many medical travel packages include complimentary airport pick-up and drop-off services. Additionally, hospital teams assist in arranging safe transportation between the hotel, hospital, and recovery accommodations.
- Multilingual Translators and Cultural Support: Most top hospitals have in-house interpreters for Arabic, French, Spanish, Russian, Swahili, and other widely spoken languages. They also assist with local cultural needs and dietary preferences.
- Affordable Guest House and Recovery Stay Options: Hospitals partner with nearby guest houses, serviced apartments, and budget hotels that offer safe and hygienic stays for patients and families. These are often within walking distance of the hospital.
- Currency Exchange and Payment Assistance: The hospital's support teams assist with currency exchange, international payment options, and guidance on utilizing health insurance (if applicable). Some hospitals even allow advance deposits through bank transfers.
- Post-Discharge Care and Follow-Up Support: Even after discharge, hospitals in India offer teleconsultation services and ongoing follow-up with the transplant team. Patients can stay connected with their doctors even after returning home.
What is the Success Rate and Survival After Liver Transplant in India?
Liver transplant outcomes in India have improved significantly, thanks to advancements in surgical techniques, experienced transplant teams, and comprehensive postoperative care. India now offers survival rates that match many leading global transplant centers, while keeping the treatment affordable.
- 1-Year Survival Rate After Liver Transplant: The average 1-year survival rate for liver transplant patients in India is between 85% and 90%. It means that the vast majority of patients recover well after the procedure, especially when the transplant is done at a reputed center with skilled specialists.
- 5-Year Survival Rate After Liver Transplant: The 5-year survival rate ranges from 70% to 75%, depending on the patient's underlying condition, age, and adherence to medications and follow-up protocols. Long-term success also depends on early detection of complications and regular monitoring.
Factors That Improve Liver Transplant Outcomes in India
Liver transplant success is higher when the procedure is performed at transplant centers with a high volume of patients and multidisciplinary teams. Early referral, optimal patient health before surgery, a compatible donor match, and consistent postoperative care also play key roles in improving survival rates.
India's Strength in Delivering High-Quality Transplants
Many Indian hospitals follow international protocols, such as those established by the AASLD (American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases) and the EASL (European Association for the Study of the Liver). The adherence to global standards, combined with state-of-the-art ICUs and access to affordable medications, helps ensure strong outcomes.
Recovery Timeline After Liver Transplant in India
Recovering from a liver transplant is a gradual process that happens in several stages. Each phase is essential for building strength, preventing complications, and adjusting to life with a new liver.
- Hospital Stay (2–3 Weeks): Most patients stay in the hospital for around 2 to 3 weeks after the transplant. The first 7–10 days are usually spent in the ICU, where doctors closely monitor the patient's condition, check liver function, and manage any signs of infection or rejection.
- Initial Home Recovery (First 3 Months): After discharge, patients need to follow strict rest and hygiene routines at home. During the first 3 months, they attend regular follow-up visits, undergo blood tests, and take medications to suppress the immune system (immunosuppressants). It is important to avoid crowded places and eat a well-balanced, low-salt diet during this time.
- Gradual Return to Routine (3–6 Months): Between 3 to 6 months, many patients begin to feel stronger and return to light activities. Doctors may reduce the dosage of certain medications, and the body starts adapting to the new liver. It's vital to closely monitor blood pressure, weight, and blood sugar levels.
- Long-Term Recovery and Lifestyle (6 Months–1 Year): By 6 to 12 months, most patients can resume work or school and return to an everyday daily life. However, long-term medication is essential, along with periodic liver function tests and check-ups. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding alcohol, eating nutritious food, and staying active, is crucial for lifelong success after transplant.
Liver Transplant Cost Comparison by Country
Compare Liver Transplant costs across different countries to make an informed decision about your medical treatment.
| Country | Cost Range (USD) | Potential Savings | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
INIndiaCurrentBest Value | $23,000 - $36,000 | — | Get Quote |
Note: Costs may vary based on hospital choice, room type, additional services, and individual medical requirements. Contact us for a personalized quote.
Leading Hospitals for Liver Transplant in India

SP Medifort Hospital
SP Medifort, Thiruvananthapuram, is a JCI-accredited, 475-bed multi-super-specialty hospital spread across 500,000 sq. ft. The hospital houses 10 modu...
Accreditations


Facilities

CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
CARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad, is a 435-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital with 120 critical care beds. Established in 20...
Accreditations

Facilities

AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad
AIG Hospitals, Gachibowli, Hyderabad, is a 1,000-bed, JCI- and NABH-accredited super-specialty hospital spanning 1.7 million sq. ft. It is the flagshi...
Accreditations


Facilities

Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai
Gleneagles Global Health City, Chennai, is a 200-bed quaternary-care hospital and part of the IHH Healthcare network, one of the world’s largest priva...
Accreditations

Facilities

MGM Healthcare, Chennai
MGM Healthcare, Chennai, is a 400-bed quaternary-care super-specialty hospital accredited by JCI, NABH, and NABL. The hospital features 100 ICU beds,...
Accreditations


Facilities

MIOT International, Chennai
MIOT International, Chennai, is a 1,000-bed NABH- and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital serving patients from more than 130 countries. Establish...
Accreditations

Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai, is the flagship hospital of the Apollo Group. Established in 1983, it has 560 beds, 46 ICUs, and 15 operating...
Accreditations



Facilities

HCG Cancer Centre, Mumbai
HCG Cancer Centre, Borivali, Mumbai, is an NABH- and AACI-accredited comprehensive cancer hospital established in 2019. The 119-bedded facility includ...
Accreditations


Facilities

Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai
Apollo Hospitals, Navi Mumbai, established in 2016, is a 500-bed JCI- and NABH-accredited quaternary care hospital offering advanced treatment across...
Accreditations


Facilities

Marengo Asia Hospitals, Faridabad
Marengo Asia Hospital, formerly QRG Health City, is a 325-bed NABH and NABL-accredited multispecialty hospital in Faridabad. It offers advanced care i...
Accreditations

Facilities
FAQ
Browse by Department
Explore procedures in different departments
Related Procedures
Other procedures in this department
Get a Free Treatment Plan
Our website uses cookies. By clicking on accept you give your consent to the use of cookies as per our Privacy Policy.
